Competitive intelligence (CI) has become central to the accuracy and credibility of market forecasting in the research industry. In today’s volatile global economy, executives rely on insights that interpret competitor behavior and structural shifts before they materialize.
According to the OECD’s Governing with Artificial Intelligence report (2025), AI systems can enhance the accuracy and timeliness of predictions by identifying complex patterns and weak signals that traditional models cannot capture. For research organizations, this convergence of intelligence and analytics is transforming forecasting into a proactive decision-support system that enables leaders to anticipate and act, not just observe.
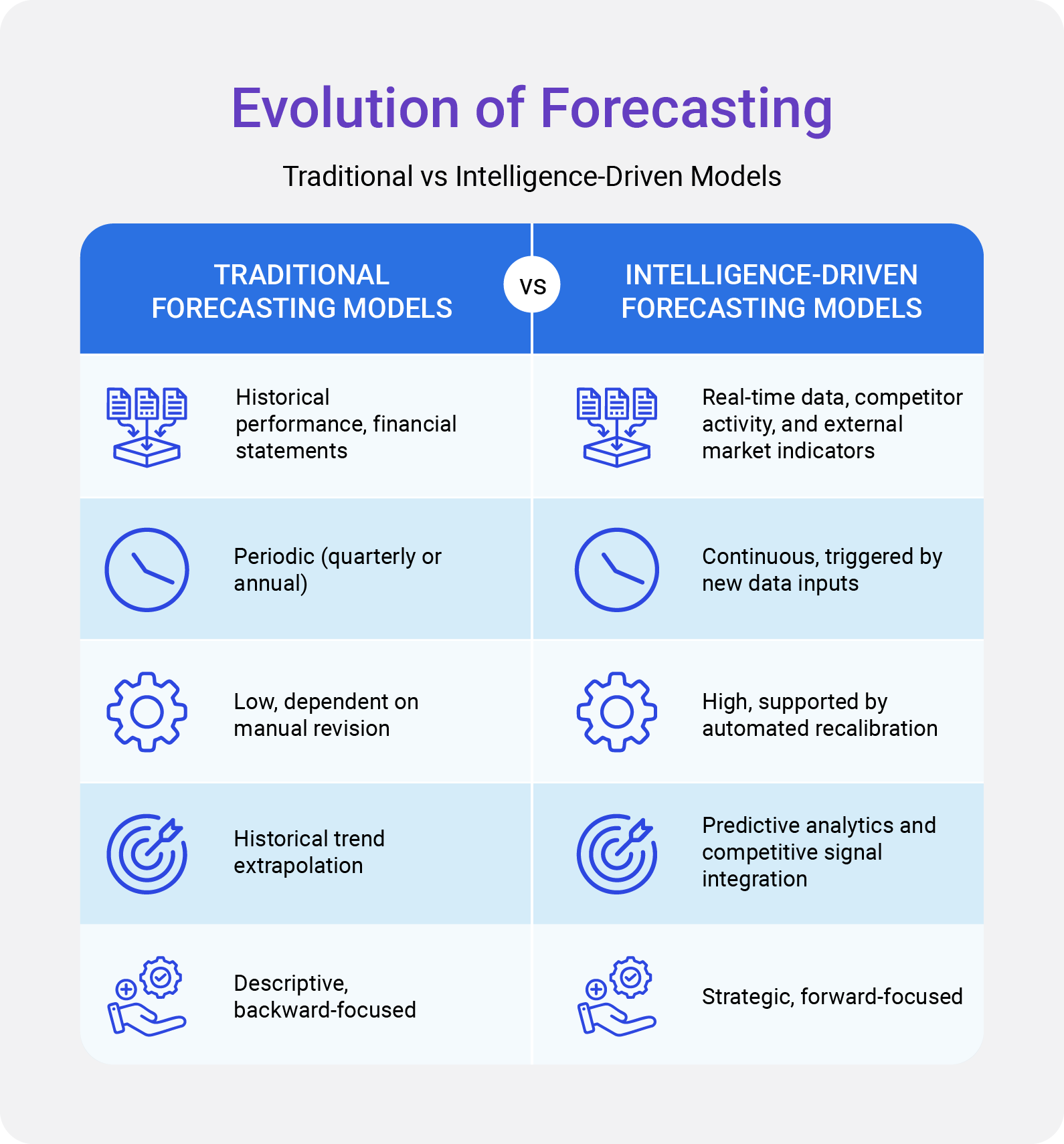
The Role of Competitive Intelligence in Forecasting
Forecasting accuracy depends on the quality and diversity of intelligence feeding the model. Competitive intelligence integrates information from multiple dimensions (pricing strategies, product introductions, supply chain movements, and policy trends) to help analysts contextualize market shifts.
The World Bank’s Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence report highlights that predictive data analysis enables organizations to interpret complex economic relationships in real time, improving responsiveness in both policy and business planning. This principle applies directly to private-sector forecasting, where competitive data serve as leading indicators of market direction.
Multi-Source Intelligence: Building a 360-Degree Market View
Modern research firms no longer rely solely on financial disclosures or survey data. Instead, they leverage open datasets from sources such as Data.gov, Eurostat, and OECD. Stat to combine trade flows, patent filings, and R&D expenditures for integrated market assessment.
According to OECD Digital Trade data, cross-border digital services trade expanded by more than 50 percent between 2015 and 2023, reshaping how firms analyze competition and forecast growth. Such multi-source integration strengthens forecast reliability by anchoring projections to measurable evidence across interconnected markets.
Forecasting Competitors Through Data Signals
AI-supported CI tools can identify early signals of change across competitive landscapes. These systems analyze variables such as production volume, export activity, and investment patterns to anticipate shifts in capacity or demand.
The U.S. Census Bureau’s Business Dynamics Statistics show that firm entry and exit rates align closely with broader economic cycles, illustrating how competitive movement reflects market momentum. When incorporated into forecasting frameworks, these datasets allow analysts to detect early signals of saturation, innovation, or disruption essential inputs for strategic planning.
For instance, a surge in raw material procurement can signal an upcoming product launch, while shifts in job postings may suggest investment in emerging technologies. When integrated into forecasting systems, these signals allow analysts to test multiple market scenarios and refine probability models. This process turns competitive intelligence into an ongoing mechanism for foresight rather than a static reporting function.
Turning Intelligence into Forecasting Strategy
The transformation of intelligence into strategy occurs when data are systematically translated into forecasting models. By aligning competitor information with macroeconomic indicators, analysts refine assumptions on market share evolution, demand elasticity, and pricing behavior.
The OECD’s research on AI in public decision-making notes that such data-driven forecasting enhances strategic alignment and resource efficiency. Within private research firms, this approach supports continuous go-to-market recalibration, enabling clients to adapt strategy in response to competitive and policy shifts.
Ethical and Transparent Intelligence Practices
The credibility of competitive intelligence depends on responsible data collection and transparent methodology. The OECD AI Principles emphasize accountability, fairness, and transparency in all data-driven systems. Similarly, ESOMAR’s Global Code of Research Ethics underscores informed consent and ethical sourcing as essential to maintaining trust. Firms adhering to these standards not only ensure compliance but also strengthen confidence in their forecasting integrity.
Business Impact: Competitive Intelligence in Action
Competitive intelligence delivers measurable advantages to organizations that embed it within their forecasting and strategy workflows.

Expanding the Scope of Competitive Insight
The progression toward intelligence-driven forecasting increasingly depends on integrating qualitative market indicators with quantitative evidence. Analyst briefings, investor communications, regulatory hearings, and technology symposiums provide forward-looking signals that quantify intent and strategic posture.
When these qualitative insights are systematically correlated with structured datasets such as trade flows, patent filings, and capital allocations, they reveal the underlying rationale driving market behavior. This enables analysts to distinguish between cyclical adjustments and structural transformation, refining both the precision and interpretive depth of forecasts. As a result, forecasting evolves into a multidimensional intelligence function that translates fragmented market data into coherent strategic foresight.
Conclusion
Competitive intelligence has reshaped forecasting from a static analytical process into a dynamic strategic discipline. The integration of open economic data, competitor monitoring, and predictive analytics produces a forward-looking framework that enhances accuracy and strategic foresight.
Evidence-based forecasting will remain critical to decision-making in data-driven economies. Kings Research advances this standard by developing transparent, adaptive, and data-grounded methodologies that reflect real market behavior and anticipate its future direction.