Market Definition
The market encompasses the global landscape of services, technologies, and solutions involved in sequencing the protein-coding regions of the genome. It includes clinical diagnostics, research applications, data analysis platforms, and associated bioinformatics services.
The market serves healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and academic research segments. The report outlines the primary drivers of market growth, along with an in-depth analysis of emerging trends and evolving regulatory frameworks shaping the industry's trajectory.
Whole exome sequencing Market Overview
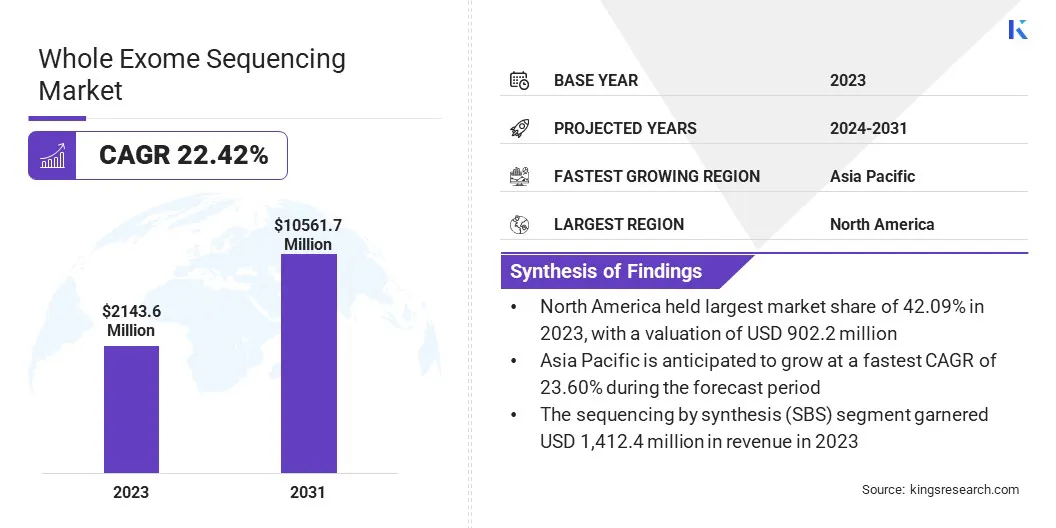
The global whole exome sequencing market size was valued at USD 2,143.6 million in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 2,563.2 million in 2024 to USD 10,561.7 million by 2031, exhibiting a robust CAGR of 22.42% over the forecast period.
This market is witnessing growth, mainly due to a surge in the demand for precision medicine and advancements in next-generation sequencing. Whole exome sequencing can efficiently identify genetic mutations linked to rare diseases, cancer, and neurological disorders.
This has made it an essential tool in clinical diagnostics and biomedical research. Increasing government funding for genomics, growing interest in population-scale genome studies, and the growing use of whole exome sequencing in translational research are further driving market expansion.
Major companies operating in the whole exome sequencing industry are Azenta Life Sciences, Caris Life Sciences, Novogene Co., Ltd., Broad Institute, Illumina, Inc., CD Genomics, Anacura, GeneMind Biosciences Co., Ltd., CENTOGENE N.V., Celemics, Inc., Ambry Genetics, GeneDx, LLC, Helix, Inc., PrivaPath Diagnostics, and Fulgent Genetics, Inc.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies are adopting whole exome sequencing for drug discovery and development, for understanding disease mechanisms and target pathways better. The widespread adoption of cloud-based bioinformatics tools has also made data interpretation easier, promoting broader use across healthcare settings.
- In January 2025, Illumina, Inc. launched the single-flow-cell NovaSeq X Sequencing System with a new software v1.3 upgrade and 25B 100-cycle and 200-cycle kits. These updates enhance multiomic capabilities and support high-throughput applications such as whole exome sequencing (WES). The software upgrade will improve sequencing accuracy, yield, and data quality, particularly for low-diversity libraries.
Key Highlights:
- The whole exome sequencing industry size was valued at USD 2,143.6 million in 2023.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 22.42% from 2024 to 2031.
- North America held a market share of 42.09% in 2023, with a valuation of USD 902.2 million.
- The services segment garnered USD 1,290.9 million in revenue in 2023.
- The sequencing by synthesis (SBS) segment is expected to reach USD 6,467.6 million by 2031.
- The diagnostics segment is expected to reach USD 5,156.8 million by 2031.
- The hospitals & clinics segment is expected to reach USD 3,993.6 million by 2031.
- The market in Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 23.60% during the forecast period.
Market Driver
"Rising Prevalence of Genetic Disorders and Technological Advancements"
The whole exome sequencing (WES) market is gaining momentum, primarily due to the rising prevalence of rare genetic disorders and cancer, rapid advancements in sequencing technologies, and decreasing costs. Genetic diseases, although rare, collectively affect millions worldwide, often leaddue to delayed or incorrect diagnoses.
Similarly, cancer requires precise genomic profiling for accurate treatment planning. WES offers comprehensive detection of variants across all coding regions of the genome, which are responsible for the majority of known disease-related mutations.
This makes it a powerful tool for diagnosing complex genetic conditions, identifying hereditary cancer syndromes, and guiding personalized treatment strategies, which increases its clinical utility and adoption.
The market is gaining acceleration by technological improvements in sequencing platforms and a consistent decline in sequencing costs. Innovations have led to faster, more accurate, and higher-throughput sequencing capabilities, making WES more affordable to hospitals, diagnostic labs, and research institutions.
Enhanced software tools for data analysis, better exome capture kits, and automation in workflows have also contributed to reducing turnaround times and simplifying the process.
Additionally, the cost of sequencing has dropped significantly over the past decade, making WES a more cost-effective solution for both routine diagnostics and large-scale research, further expanding its reach across developed and emerging healthcare markets.
- In February 2025, Roche unveiled its proprietary sequencing by expansion (SBX) technology, marking the introduction of a new category in next-generation sequencing. This technology uses expanded synthetic molecules called Xpandomers and a high-throughput sensor module to enable ultra-rapid, scalable, and flexible sequencing. This advancement aims to significantly accelerate genomic research and clinical applications by reducing sequencing time from days to hours.
Market Challenge
"Complexity of Data Interpretation and Lack of Standardization"
A major challenge in the whole exome sequencing market is the accurate interpretation of complex genetic data, compounded by the absence of standardized analytical protocols.
Although WES targets only 1 to 2% of the human genome, which is the protein-coding region known as the exome, it captures more than 85% of known disease-causing mutations, generating a large number of genetic variants per individual. Most of these variants are benign, but some may be pathogenic or classified as variants of uncertain significance (VUS).
This makes interpreting them highly challenging. To differentiate clinically actionable mutations from benign or ambiguous variants, a deep expertise, access to large population datasets, and integration with clinical context is necessary.
This involves a time-consuming manual review. Further complicating this challenge is the inconsistent classification of genetic variants across laboratories and platforms due to inconsistency in algorithms, interpretive guidelines, and reference databases. This lack of standardization leads to conflicting results and lower diagnostic confidence.
A viable solution lies in the adoption of advanced bioinformatics pipelines and AI-powered variant interpretation tools, which streamline data analysis and improve consistency. AI can rapidly filter and prioritize variants based on phenotype relevance and existing literature, while predictive modeling can help in a more accurate classification.
Market Trend
"AI Integration and Expanding Applications in Newborn and Population Genomics"
The integration of WES with artificial intelligence (AI) and bioinformatics, and its expanding adoption in newborn screening and population genomics programs is a major trend driving the market. The use of AI and advanced bioinformatics tools is transforming how WES data is processed, interpreted, and applied in clinical and research settings.
AI helps analyze the large and complex data from WES much faster and more accurately. It finds important genetic changes and helps sort them into useful categories automatically.
This reduces the time from sequencing to diagnosis and improves the reliability and reproducibility of results, enabling more precise and efficient decision-making in personalized medicine.
- In February 2025, BioAro launched its AI-powered PanOmiQ platform, an ultrafast genomic analysis solution capable of analyzing Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) and Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) data in under 2 hours. The platform generates Variant Call Format (VCF) files in under 5 minutes and integrates AI-driven analytics to enhance accuracy and accessibility of precision medicine. PanOmiQ also includes real-time microbiome analysis, enabling advanced applications in cancer research, rare disease diagnostics, and personalized healthcare.
At the same time, more people are exploring how WES can help with early disease detection and prevention. This includes its use in newborn screening and big population health studies. WES identifies potentially life-threatening or manageable genetic conditions in infants early on and enable timely interventions.
On a broader scale, population genomics programs are leveraging WES to map genetic diversity, understand disease risk at a population level, and guide public health strategies. These applications highlight WES's expanding role beyond traditional diagnostics, positioning it as a foundational tool in proactive and predictive healthcare models.
Whole exome sequencing Market Report Snapshot
|
Segmentation
|
Details
|
|
By Product & Service
|
Services, Kits & Reagents, Sequencing Platforms
|
|
By Technology
|
Sequencing by Synthesis (SBS), Ion Semiconductor Sequencing
|
|
By Application
|
Diagnostics, Drug Discovery & Development, Personalized Medicine
|
|
By End User
|
Academic & Research Institutes, Hospitals & Clinics, Biotechnology
|
|
By Region
|
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico
|
|
Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe
|
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific
|
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa
|
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America
|
Market Segmentation
- By Product & Service (Services, Kits & Reagents, and Sequencing Platforms): The services segment earned USD 1,290.9 million in 2023 due to the growing demand for outsourced sequencing and data interpretation in clinical and research settings.
- By Technology (Sequencing by Synthesis (SBS), Ion Semiconductor Sequencing): The Sequencing by Synthesis (SBS) segment held 65.89% of the market in 2023, due to its high accuracy, scalability, and widespread adoption in clinical genomics.
- By Application (Diagnostics, Drug Discovery & Development, and Personalized Medicine): The diagnostics segment is projected to reach USD 5,156.8 million by 2031, owing to the increasing prevalence of genetic disorders and the integration of genomic testing into routine healthcare.
- By End User (Academic & Research Institutes, Hospitals & Clinics, and Biotechnology): The Hospitals & Clinics segment is projected to reach USD 3,993.6 million by 2031, owing to the rising use of genomic data for patient-specific diagnosis and treatment planning.
Whole Exome Sequencing Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America.
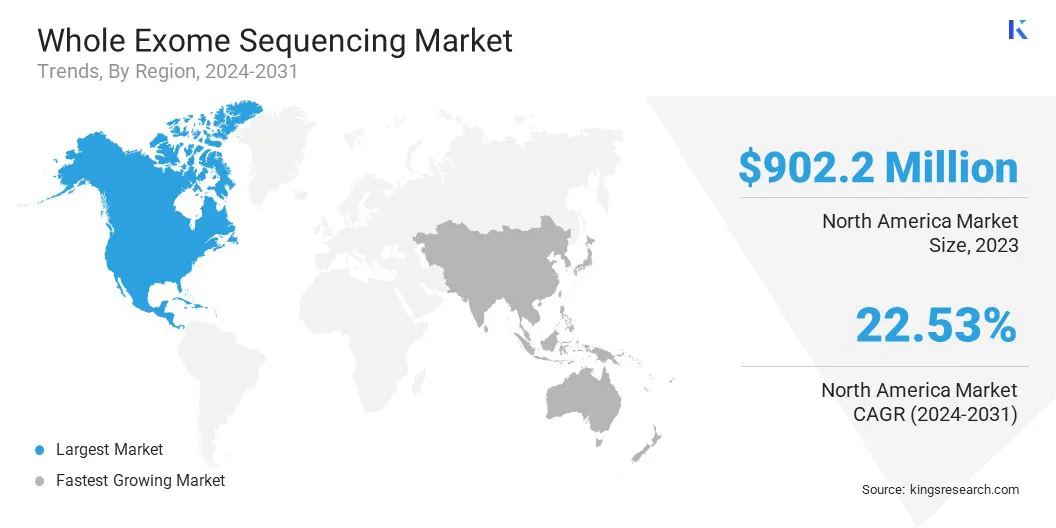
North America whole exome sequencing market share stood at around 42.09% in 2023 in the global market, with a valuation of USD 902.2 million. This is due to the strong presence of leading sequencing service providers, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and a high concentration of academic and clinical research institutions across the U.S. and Canada.
The region also benefits from early adoption of next-generation sequencing technologies. The integration of WES into clinical practice by major hospitals and cancer centers, particularly for oncology and rare disease diagnostics, has further fueled market growth.
Additionally, the presence of large-scale genomic initiatives and collaborations between healthcare systems and biotech firms has driven the demand for sequencing services.
The whole exome sequencing industry in Asia Pacific is expected to register the fastest growth with a projected CAGR of 23.60% over the forecast period. This expansion is driven by the increasing prevalence of genetic disorders, expanding research capabilities, and rising investment by local biotech companies in China, India, South Korea, and Japan.
In China, the development of domestic sequencing platforms and emerging genomic service startups have made whole exome sequencing more affordable and accessible.
Meanwhile, India is witnessing growing adoption in academic and diagnostic laboratories, driven by a rising burden of inherited diseases and growing awareness of genomic medicine. Japan and South Korea are also using technological innovation and promoting partnerships between academia and industry, further propelling regional growth.
The region's large and genetically diverse population also presents a unique opportunity for population-scale studies, increasing the demand for exome sequencing solutions.
Regulatory Frameworks
- In the U.S., whole exome sequencing is regulated under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), which ensures the quality and reliability of laboratory testing, and by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for oversight of diagnostic devices and tests. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) governs the privacy and security of genetic data.
- In the EU, whole exome sequencing is regulated by the In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices Regulation (IVDR), which classifies and sets requirements for genetic tests, and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which strictly controls the use and sharing of genetic information.
- In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates genetic testing technologies, including exome sequencing, while the Measures for the Administration of Human Genetic Resources control access, use, and export of genetic data.
- In Japan, whole exome sequencing is subject to regulation under the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act (PMDA), which evaluates genetic diagnostic tools, and is supported by ethical guidelines from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) on personal genomic data.
- In India, whole exome sequencing is guided by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), draft rules are being discussed to ensure genomic data is used ethically. These rules also aim to follow the Information Technology Act to keep the data safe and protected.
Competitive Landscape
The whole exome sequencing industry is characterized by rapid innovation, as key players focus on strategic initiatives to strengthen their market position. Companies are investing in expanding their sequencing service portfolios by enhancing throughput, accuracy, and turnaround times to meet diverse customer needs.
Strategic collaborations and partnerships with academic institutions, clinical research organizations, and healthcare providers are commonly used to broaden application reach and access large genomic datasets.
A notable strategy is vertical integration combining sequencing platforms, reagents, and bioinformatics tools into streamlined solutions to offer end-to-end services. Additionally, market players are focusing on geographic expansion, targeting high-growth regions such as Asia Pacific and Latin America, by setting up local facilities and distribution networks.
The launch of cost-effective and scalable sequencing kits tailored for diagnostic labs and smaller institutions is also being done to reach emerging segments. Furthermore, continued efforts in R&D and proprietary data analysis algorithms are being used to enhance interpretation accuracy and maintain a competitive edge.
- In March 2025, Genomize and Genomenon partnered to integrate data from Genomenon’s Mastermind Genomic Intelligence Platform and Cancer Knowledge Base (CKB) into Genomize’s SEQ Platform. The collaboration aims to enhance genomic interpretation by incorporating expertly curated germline and somatic variant data, enabling researchers and clinicians to derive more precise and actionable insights from next-generation sequencing (NGS) data, including whole exome sequencing.
List of Key Companies in Whole Exome Sequencing Market:
- Azenta Life Sciences
- Caris Life Sciences
- Novogene Co., Ltd.
- Broad Institute
- Illumina, Inc.
- CD Genomics
- anacura
- GeneMind Biosciences Co., Ltd.
- CENTOGENE N.V.
- Celemics, Inc.
- Ambry Genetics
- GeneDx, LLC
- Helix, Inc.
- PrivaPath Diagnostics
- Fulgent Genetics, Inc.
Recent Developments (Investment/Product Launches)
- In April 2025, Caris Life Sciences raised USD 168 million in private capital from leading investors to expand its precision medicine platform. The funding will support the growth of MI Cancer Seek. It is the first test to combine Whole Exome and Whole Transcriptome Sequencing with FDA-approved CDx use. The funding will also help expand Caris Assure, a simple blood test that uses the same technology to guide cancer treatment.
- In October 2024, Element Biosciences, Inc. launched Trinity, a novel exome target capture solution designed to simplify and accelerate whole exome sequencing workflows. Trinity integrates capture, wash, and sequencing steps directly onto the AVITI System, reducing manual processing time and enabling same-day sequencing with 1-hour hybridization. The company partnered with Integrated DNA Technologies and Twist Bioscience to supply exome-targeting tools for the Trinity workflow.
- In August 2024, Ambry Genetics announced the launch of ExomeReveal, a new multiomic exome sequencing test that combines DNA and RNA analysis to improve rare disease detection. The test enhances diagnostic yield by incorporating RNA functional studies to resolve variants of uncertain significance, marking a significant advancement in clinical exome testing for patients with complex genetic conditions.
- In May 2024, Baylor Genetics launched a new RNA sequencing (RNAseq) test as a reflex analysis for Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) and Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS), enhancing the interpretation of Variants of Uncertain Significance (VUS). The company also reduced standard turnaround times for WES and WGS to 3 weeks, with rapid results available in 5 days, and introduced four new genetic analysis panels targeting specific disorders.


