Market Definition
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic liver disease characterized by inflammation and fibrosis of the bile ducts, leading to impaired bile flow and liver damage. Current treatment approaches focus on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and delaying disease progression through medication, endoscopic therapy, or liver transplantation.
Its scope includes pharmaceutical therapies, biologics, and supportive care targeting immune modulation and bile acid regulation. Hospitals, specialty clinics, and research institutions provide these treatments to improve patient survival and quality of life.
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Market Overview
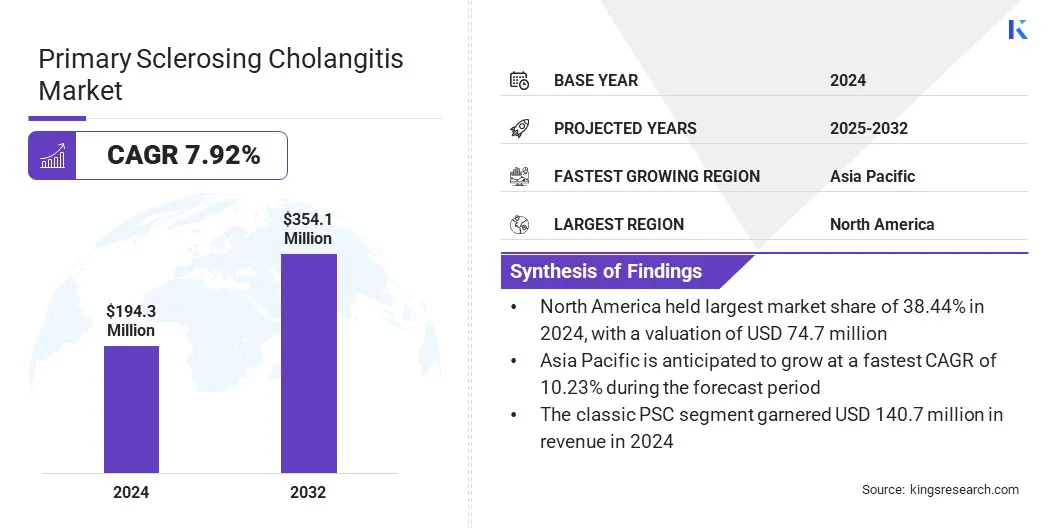
According to Kings Research, the global primary sclerosing cholangitis market size was valued at USD 194.3 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 207.6 million in 2025 to USD 354.1 million by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 7.92% during the forecast period.
This growth is driven by advancements in diagnostic imaging and biomarker technologies that enable earlier and more accurate disease detection. The integration of genomic and microbiome research is also identifying novel therapeutic targets, supporting the development of precision-based treatments and accelerating progress in clinical research.
Key Market Highlights:
- The primary sclerosing cholangitis industry was valued at USD 194.3 million in 2024.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.92% from 2025 to 2032.
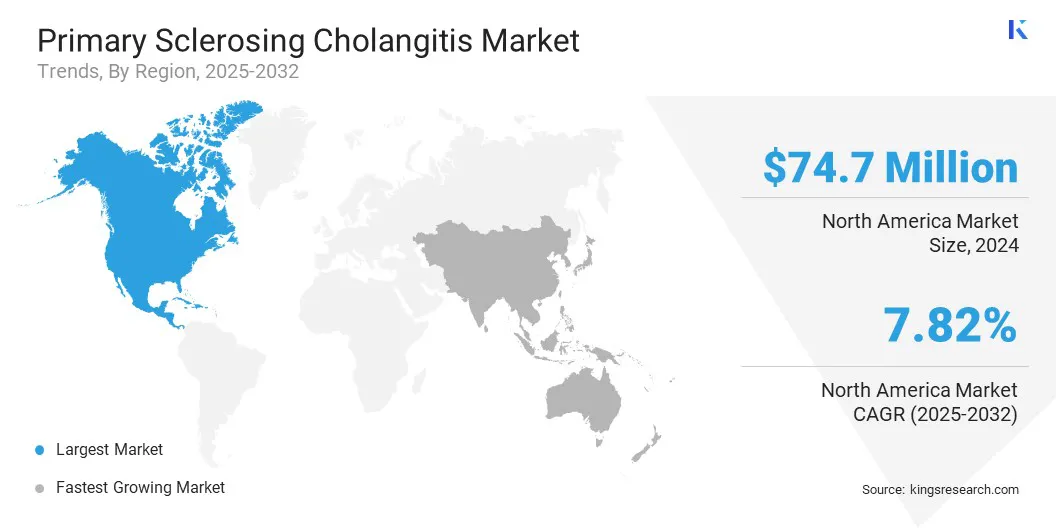
- North America held a share of 38.44% in 2024, valued at USD 74.7 million.
- The classic PSC segment garnered USD 140.7 million in revenue in 2024.
- The ursodeoxycholic acid segment is expected to reach USD 137.2 million by 2032.
- The hospital pharmacies segment secured the largest revenue share of 58.92% in 2024.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 10.23% over the forecast period.
Major companies operating in the primary sclerosing cholangitis market are Esperion Therapeutics, Inc., Pliant Therapeutics, Inc., Dr. Falk Pharma GmbH, Chemomab Therapeutics Ltd., CuromeBiosciences, LISCure, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., Ipsen Pharma, Gilead Sciences, Inc., Mirum Pharmaceuticals, HighTide Therapeutics, Inc., and Cascade Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Rising prevalence of liver and biliary disorders is positively influencing the market. Rising cases of autoimmune liver diseases and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are leading to higher PSC diagnosis rates. This surge in diagnoses is prompting healthcare providers to implement more frequent monitoring and early intervention strategies.
- In September 2024, a study funded by the Birmingham NIHR Biomedical Research Centre reported that the prevalence of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) with a prior inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) diagnosis was 5.0 per 100,000 population in 2015, increasing to 5.7 when including individuals who developed IBD after PSC. By 2020, the prevalence rose to 7.6 per 100,000 (8.6 when accounting for IBD developing after PSC), representing an average annual growth of 8.8. The study projected that by 2027, PSC-IBD prevalence will reach 11.7 per 100,000, or 13.3 when accounting for IBD cases developing after PSC.
Improved screening techniques and diagnostic tools are enabling clinicians to detect PSC at earlier stages. Increased awareness among medical professionals about the association between IBD and PSC is further improving patient identification.
What factors are boosting the growth of the primary sclerosing cholangitis market?
Advancements in diagnostic imaging and biomarker technologies are fueling the growth of the market. Increasing adoption of MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography) is improving non-invasive visualization of bile ducts.
This enhanced imaging capability supports earlier and more accurate detection of PSC. Simultaneously, emerging serum biomarkers are enabling precise monitoring of disease progression.
In June 2024, a study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences reported that serum levels of the chemokine CCL24 had an AUROC > 0.9 for distinguishing PSC presence and > 0.8 for staging through the ELF fibrosis score in PSC patients.
Combining advanced imaging and biomarkers is helping clinicians differentiate PSC from other liver disorders effectively. These improvements in diagnosis and monitoring are increasing demand for PSC-related healthcare solutions.
- In November 2024, Perspectum Ltd received a grant from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to evaluate a novel imaging-biomarker for PSC, correlating quantitative Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP+) metrics with clinical outcomes.
What challenges arise from the lack of curative therapies?
A key challenge impeding the expansion of the primary sclerosing cholangitis market is the absence of approved curative therapies, leaving current treatments largely supportive.
Patients rely on symptom management, which does not halt disease progression or prevent complications such as liver failure and cholangiocarcinoma. This treatment gap increases the clinical and economic burden on healthcare systems and affects patients’ quality of life.
To address this challenge, market players are investing in targeted drug development, conducting clinical trials for novel therapies, and exploring repurposing existing medications for PSC. These efforts are advancing potential disease-modifying options and improving long-term management strategies for patients.
- In May 2025, Chemomab Therapeutics, Ltd. reported positive results from its Phase 2 SPRING trial of Nebokitug (CM‑101) in PSC, showing favorable tolerance and notable biomarker improvements associated with fibrosis and inflammation over 48 weeks.
Which emerging trends are driving advancements in PSC research?
A key trend influencing the primary sclerosing cholangitis market is the integration of genomic and microbiome research to advance disease understanding and therapeutic development. Researchers are increasingly focusing on multi-omics approaches to link genetic predisposition with immune dysregulation and bile duct inflammation.
Growing evidence connecting the gut-liver axis to disease pathology is highlighting the role of microbial imbalance in disease onset and progression. These findings are supporting the identification of novel biomarkers that improve diagnostic accuracy and enable patient segmentation for clinical trials.
Pharmaceutical companies are aligning research efforts with academic institutions to apply genomic and microbiome insights in developing precision-based therapies.
- A May 2024 study published in BMC Gastroenterology examined the links between genetics, metabolites, and gut microbiota in PSC. The research revealed that higher genetically predicted levels of the lipid metabolite phosphatidylcholine were associated with an increased risk of PSC, with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.30 and a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 1.03–1.63, indicating a statistically significant 30% higher risk. The study estimated that approximately 17.6% of this genetic effect on PSC risk was mediated through the bacterium Eubacterium rectale.
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Market Report Snapshot
|
Segmentation
|
Details
|
|
By Type
|
Classic PSC, Small-duct PSC, PSC Associated with Autoimmune Hepatitis
|
|
By Drug Class
|
Ursodeoxycholic Acid, Obeticholic Acid, Methotrexate, Corticosteroids, Others
|
|
By Distribution Channel
|
Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies
|
|
By Region
|
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico
|
|
Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe
|
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific
|
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, U.A.E., Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa
|
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America
|
Market Segmentation
- By Type (Classic PSC, Small-duct PSC, PSC Associated with Autoimmune Hepatitis): The classic PSC segment earned USD 140.7 million in 2024, mainly due to its higher prevalence and the availability of established diagnostic protocols that enable early detection and consistent clinical management.
- By Drug Class (Ursodeoxycholic Acid, Obeticholic Acid, Methotrexate, Corticosteroids, and Others): The ursodeoxycholic acid segment held a share of 41.32% in 2024, fueled by its proven efficiency in improving liver function, reducing bile toxicity, and showing disease progression among patients with limited treatment alternatives.
- By Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Online Pharmacies): The hospital pharmacies segment is projected to reach USD 204.5 million by 2032, owing to the wider availability of specialized therapies and the need for continuous monitoring and administration of advanced therapeutic drugs in clinical settings.
Based on region, the global market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America.
What regional factors are propelling PSC market expansion?
The North America primary sclerosing cholangitis market share stood at 38.44% in 2024, valued at USD 74.7 million. This dominance is reinforced by a strong network of research institutions and active clinical trials focused on developing new therapies and optimize existing treatments.
These trials generate robust clinical evidence, supporting faster adoption of innovative drugs. Increased trial activity also attracts global pharmaceutical investment, propelling regional market growth.
- In April 2025, the Phase 2 ELMWOOD trial evaluating elafibranor for treating PSC reported positive results. Conducted across North America and Europe with 68 patients aged 18–75, the 12-week study assessed daily doses of 80 mg or 120 mg versus placebo and showed that elafibranor significantly reduced pruritus, a major symptom in PSC patients.
The primary sclerosing cholangitis industry in Asia Pacific is poised to grow at a CAGR of 10.23% over the forecast period. This growth is fostered by the rapid development of hepatology and gastroenterology centers.
Modern facilities offering comprehensive PSC management, including endoscopic procedures and transplant services, have improved access to specialized care, enabling timely and effective treatment. Additionally, the increasing number of tertiary care hospitals contributes to higher adoption of both conventional and novel therapies, fueling market expansion.
- In September 2024, KPJ Damansara Specialist Hospital partnered with Mayo Clinic Care Network, which enhances the hospital's capabilities in providing specialized care, including gastroenterology and hepatology services. The partnership facilitates access to Mayo Clinic's medical expertise and resources, supporting the hospital's commitment to delivering advanced treatments for liver diseases such as PSC.
Regulatory Frameworks
- In the U.S., the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval and regulation of drugs and biologics for PSC. The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) provides evidence-based guidelines for the diagnosis and management of PSC. These guidelines are regularly updated to reflect the latest research and clinical practices.
- In Germany, the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM) governs the approval of PSC therapies. Regulatory oversight facilitates clinical research, adoption of novel therapies, and structured disease management across specialized healthcare centers.
- In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates the approval of drugs and biologics for PSC. The NMPA evaluates clinical trial data to ensure the safety and efficacy of treatments. The NMPA also monitors the safety of drugs through post-marketing surveillance and adverse event reporting systems.
- In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW), supported by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), supervises PSC therapies. The PMDA evaluates trial data to ensure safety and efficacy, while post-marketing surveillance monitors outcomes.
Competitive Landscape
Major players are adopting strategies such as research and development, strategic partnerships, and technological advancements to remain competitive in the primary sclerosing cholangitis market. Companies are increasingly focusing on developing novel therapies that target specific disease pathways and improve patient outcomes.
Collaborations with research institutions and clinical centers enable faster clinical trial execution and knowledge sharing. Investment in advanced drug delivery systems and precision medicine approaches is also helping companies differentiate their offerings and maintain a strong position in the market.
- In April 2025, Esperion presented new research on treatments for primary sclerosing cholangitis, a rare liver disorder during its R&D Day. The company highlighted its lead candidates, including ESP-1336, which are novel allosteric inhibitors of ATP citrate lyase (ACLY) designed to address hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. It presented data suggesting that its oral therapies could modulate pathways involved in PSC pathogenesis.
List of Key Companies in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Market:
- Esperion Therapeutics, Inc.
- Pliant Therapeutics, Inc.
- Falk Pharma GmbH
- Chemomab Therapeutics Ltd.
- CuromeBiosciences
- LISCure
- NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Ipsen Pharma
- Gilead Sciences, Inc.
- Mirum Pharmaceuticals
- HighTide Therapeutics, Inc.
- Cascade Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Recent Developments
- In October 2025, Esperion Therapeutics introduced the ESP-2001 as a preclinical development candidate for the treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). ESP-2001 is a highly specific allosteric inhibitor of ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), targeting key pathways involved in liver inflammation and fibrosis.
- In May 2025, Pliant Therapeutics announced positive Phase 2a results for bexotegrast in PSC. The oral integrin inhibitor showed improvements in cholestasis markers and stabilized liver fibrosis in PSC patients. Bexotegrast's mechanism of action targets key pathways in fibrosis progression, offering a novel approach to PSC treatment.
- In April 2024, LISCure Biosciences received Fast Track Designation from the FDA for its investigational oral therapy, LB-P8, developed for PSC. The drug targets liver inflammation and fibrosis, with the designation aimed at expediting its clinical development and regulatory review to accelerate patient access.


