Market Definition
An incinerator is a specialized high-temperature combustion system that converts waste materials into ash, gases, and heat. It is used for the safe disposal of municipal solid waste, hazardous waste, medical waste, and industrial by-products.
Incineration reduces waste volume, minimizes the risk of contamination, and helps generate energy through heat recovery. The market includes the manufacturing, installation, operation, and maintenance of various incineration systems.
Incinerator Market Overview
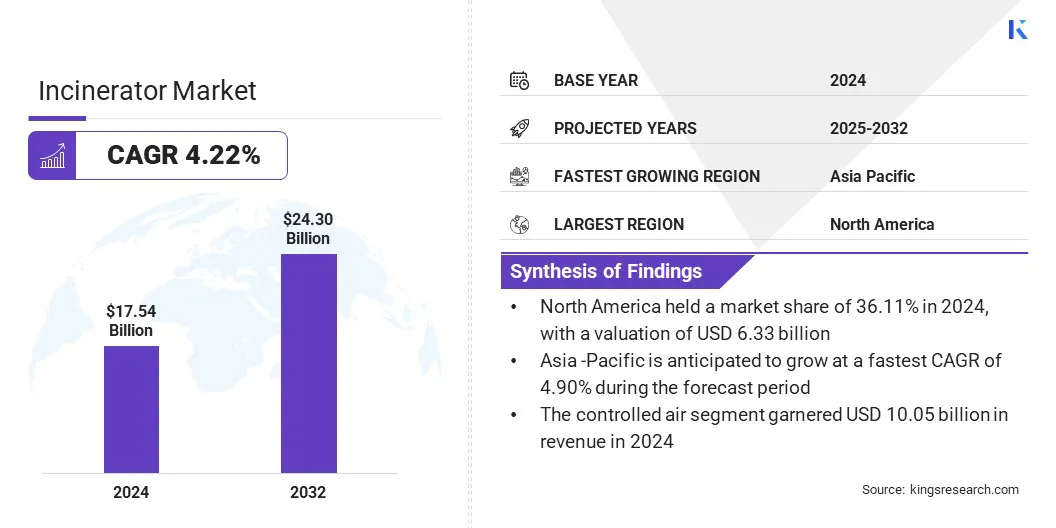
The global incinerator market size was valued at USD 17.54 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 18.19 billion in 2025 to USD 24.30 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.22% over the forecast period.
Market growth is driven by the growing demand for sustainable waste management solutions that reduce municipal, industrial, and hazardous waste. The rising use of energy-from-waste (EfW) incineration systems for renewable energy generation is further supporting the integration of advanced waste-to-energy technologies across municipal, industrial, and hazardous waste sectors.
Key Highlights:
- The incinerator industry size was recorded at USD 17.54 billion in 2024.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.22% from 2025 to 2032.
- North America held a share of 36.11% in 2024, valued at USD 6.33 billion.
- The moving grate segment generated USD 7.23 billion in revenue in 2024.
- The municipal solid waste segment is expected to reach USD 9.73 billion by 2032.
- The excess air segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of 4.94% over the forecast period.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.90% over the forecast period.
Major companies operating in the incinerator market are Alfa Therm Limited, G&O Maritime Group, Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc, CHUWASTAR, Dutch Incinerators BV, ECO Concepts, Haat Incinerators India Pvt Ltd, Yell Limited, Inciner8 Limited, Keller Manufacturing, Inc, Ketek Group, Maximus Envirotech Pvt. Ltd, MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD, SUEZ SA, and Vikas Engineering.
The growing focus on sustainable waste management and resource recovery is increasing the use of advanced incineration technologies. Furthermore, rising investments in incinerator bottom ash processing and recycling capabilities are improving overall efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and creating new growth opportunities for market players.
- In July 2025, Blue Phoenix Group acquired Meldgaard Recycling’s incinerator bottom ash (IBA) business expanding its presence in Denmark. This will strengthen its global core business of IBA processing, improving expertise in sustainable waste management and resource recovery.
Market Driver
Increasing Municipal Solid Waste Generation
A key factor pushing the growth of the incinerator market is the increasing municipal solid waste due to rapid urbanization and population growth. Rising waste levels are creating pressure on existing waste management systems and increasing landfill dependency. This is prompting governments and industries to adopt efficient waste treatment solutions such as incineration, which reduces waste volume, recovers energy, and supports sustainable disposal.
- The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) in its “Global Waste Management Outlook 2024” stated that the annual global municipal solid waste (MSW) generation is projected to increase from about 2.1 billion tonnes in 2023 to 3.8 billion tonnes by 2050.
Market Challenge
High Capital and Operational Costs
A key challenge hampering the growth of the incinerator market is the high capital and operational costs compared to alternative waste management methods. Establishing an incineration facility requires substantial investment in advanced combustion systems, pollution control technologies, and compliance with strict environmental regulations.
Additionally, ongoing expenses for fuel, maintenance, skilled labor, and monitoring systems raise operational costs. These financial burdens restrict adoption and delay the widespread deployment of incineration as an effective and sustainable waste disposal solution.
To address this, market players are investing in advanced, cost-efficient technologies and modular incineration systems that reduce installation and maintenance expenses. Companies are developing energy-from-waste solutions to recover energy and offset operational costs, while integrating automation and smart monitoring to improve productivity.
Market Trend
Increasing Adoption of Automated Monitoring and Smart Incineration Systems
A notable trend in the incinerator market is the increasing use of automated monitoring and smart incineration systems. These systems integrate advanced automation, IoT-enabled tracking, and real-time data analytics. Smart incinerators enable remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and precise control of combustion processes, improving operational performance while reducing emissions.
- In November 2024, Neo San launched the Neo‑AX, a decentralized high-efficiency incinerator designed for biomedical, municipal, sanitary, and industrial waste. The system operates at 1,200°C, produces sterile ash with low environmental impact, and features automation, robust safety mechanisms, and IoT-enabled real-time tracking of waste and emissions.
Incinerator Market Report Snapshot
|
Segmentation
|
Details
|
|
By Type
|
Moving Grate, Rotary Kiln, Fluidized Bed, Static Hearth and Multiple Hearth
|
|
By Application
|
Municipal Solid Waste, Hazardous Waste, Medical Waste, Industrial Waste, Others
|
|
By Operation
|
Controlled Air, Excess Air
|
|
By Region
|
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico
|
|
Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe
|
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific
|
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, U.A.E., Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa
|
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America
|
Market Segmentation:
- By Type (Moving Grate, Rotary Kiln, Fluidized Bed, and Static Hearth and Multiple Hearth): The moving grate segment earned USD 7.23 billion in 2024 due to its efficiency in handling large volumes of heterogeneous waste with lower operational costs.
- By Application (Municipal Solid Waste, Hazardous Waste, Medical Waste, Industrial Waste, and Others): The municipal solid waste segment held 42.10% of the market in 2024, due to rapid urbanization, rising waste generation, and strong demand for waste-to-energy solutions.
- By Operation (Controlled Air, and Excess Air): The controlled air segment is projected to reach USD 13.29 billion by 2032, owing to its superior combustion control, lower emissions, and adaptability to various waste types.
Incinerator Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America.
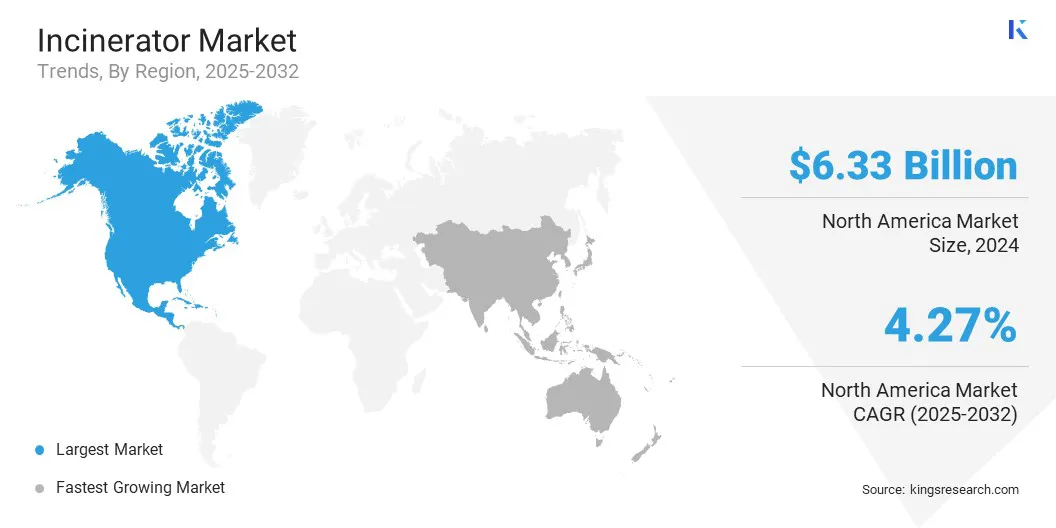
The North America incinerator market share stood at 36.11% in 2024, valued at USD 6.33 billion. This dominance is driven by the increasing municipal solid waste, which is prompting demand for waste-to-energy and disposal solutions. Strict environmental regulations governing hazardous and medical waste management are accelerating the adoption of advanced incineration technologies.
The growing healthcare sector waste, particularly infectious and biomedical waste, is driving the need for safe and compliant treatment options to protect public health and the environment. Additionally, regional players are increasing investments in incineration facilities to increase efficiency, improve emissions control, and develop specialized waste treatment capabilities.
- In October 2024, Arcwood Environmental Services acquired EBV Explosives Environmental Company, Inc., a leading energetic waste disposal provider in North America. The acquisition adds a facility equipped with a rotary kiln incinerator, a car bottom furnace, and 11 thermal treatment units. It also increases Arcwood’s capabilities in demilitarization and explosives incineration while expanding its presence in the market.
Asia Pacific is set to grow at a CAGR of 4.90% over the forecast period. This growth is driven by rapid urbanization and population growth across region, which increases municipal solid waste and creates demand for efficient waste treatment solutions.
Expansion of the healthcare and manufacturing sectors is increasing the need for specialized waste management systems. Additionally, growing investments by market players in large-scale waste treatment infrastructure are improving the processing capacity and competence of incineration facilities, supporting market growth.
- In June 2024, Séché Environnement signed an agreement to acquire ECO Industrial Environmental Engineering Pte Ltd, Singapore’s leading hazardous industrial waste company. The acquisition adds a 68,400 m² facility with incinerators, industrial water treatment, and stabilization plants, providing an annual capacity of nearly 440 Kt.
Regulatory Frameworks
- In the U.S., the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates incinerators under the Clean Air Act, setting emission standards for hazardous and municipal solid waste incinerators. The EPA requires that hazardous waste incinerators achieve a destruction efficiency of 99.99% or higher. It also mandates that incinerators monitor and report toxic emissions, including dioxins and nitrogen oxides, to the Toxics Release Inventory. Additionally, the EPA oversees permitting processes and ensures compliance with federal environmental standards.
- In the UK, the Environment Agency regulates waste incineration under the Environmental Permitting Regulations. It issues permits for incineration facilities, ensuring they meet strict environmental standards. The Environment Agency monitors emissions from incinerators, including pollutants such as nitrogen oxides and dioxins, to protect air quality and public health.
- In China, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) is the primary authority for setting and enforcing national environmental standards for waste incineration and emissions. The MEE develops regulations and guidelines to control air pollutants from incineration facilities. It also monitors compliance with these standards and conducts environmental impact assessments for new incineration projects.
- In India, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is responsible for regulating incineration practices under the Hazardous and Other Wastes (Management and Transboundary Movement) Rules. The CPCB sets standards for the design, operation, and emission limits of hazardous waste incinerators. It also issues guidelines for biomedical waste incinerators and conducts inspections to ensure compliance.
Competitive Landscape
Major players in the incinerator industry are expanding their operational capacities by developing new facilities equipped with advanced combustion and emissions control. They are investing in technological innovation, integrating automation, IoT-enabled monitoring, and energy recovery systems to improve safety and compliance with environmental standards.
Companies are also strengthening regional presence through strategic expansions and upgrades, improving access to specialized waste streams such as medical, hazardous, and industrial waste. Additionally, they are focusing on sustainable practices by using modern infrastructure that reduces environmental impact and improves the process.
- In October 2024, Stericycle opened a USD 110 million, 110,000 square foot medical waste incineration facility in McCarran, Nevada. The facility expands Stericycle’s capacity for regulated medical waste treatment and strengthens its North American operations for sustainable incineration practices.
Key Companies in Incinerator Market:
- Alfa Therm Limited
- G&O Maritime Group
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc
- CHUWASTAR
- Dutch Incinerators BV
- ECO Concepts
- Haat Incinerators India Pvt Ltd
- Yell Limited
- Inciner8 Limited
- Keller Manufacturing, Inc
- Ketek Group
- Maximus Envirotech Pvt. Ltd
- MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD
- SUEZ SA
- Vikas Engineering.
Recent Developments
- In June 2025, Veolia acquired three leading waste management companies in Massachusetts and California. The acquisitions include New England Disposal Technologies, New England MedWaste, and Ingenium. This supports Veolia’s capabilities in high-temperature hazardous waste treatment and disposal.


