Market Definition
Robotic welding refers to the use of automated systems and equipment that perform welding operations using programmable robotic arms and advanced control technologies. It includes robotic manipulators, welding torches, power sources, sensors, and control units that work together to execute precise and consistent welds.
These systems are used to join metal parts in applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and heavy machinery manufacturing. Robotic welding ensures high-quality, consistent welds while improving production efficiency, operator safety, and cost-effectiveness throughout the fabrication process.
Robotic Welding Market Overview
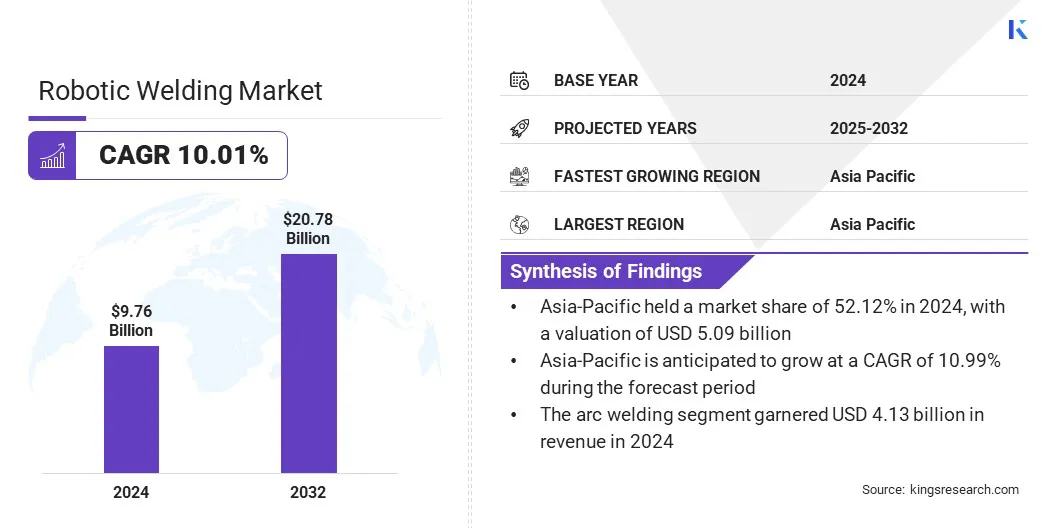
The global robotic welding market size was valued at USD 9.76 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 10.66 billion in 2025 to USD 20.78 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 10.01% over the forecast period.
The market is experiencing a strong growth driven by the rising automation in manufacturing and the increasing adoption of robotic welding in automotive and heavy industries. Advancements in sensor and AI-based control systems are also enhancing welding precision and productivity.
Key Highlights:
- The robotic welding industry size was recorded at USD 9.76 billion in 2024.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.01% from 2025 to 2032.
- Asia Pacific held a market share of 52.12% in 2024, with a valuation of USD 5.09 billion.
- The arc welding segment generated USD 4.13 billion in revenue in 2024.
- By Payload Capacity, the up to 50 kg segment is expected to reach USD 9.03 billion by 2032.
- The up to 50 kg payload capacity segment is projected to attain a market value of USD 9.03 billion by 2032.
- The electrical & electronics segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of 11.78% over the forecast period.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 10.99% over the forecast period.
Major companies operating in the robotic welding market are ABB, Fanuc Corporation, Yaskawa America, Inc., KUKA SE & Co. KGaA, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Comau S.p.A., DENSO Robotics, Nachi-fujikoshi corp., Panasonic Connect Co., Ltd., The Lincoln Electric Company, Illinois Tool Works Inc., CLOOS Welding Technology GmbH, Fronius International GmbH, and OTC Daihen Inc.
A key factor driving the market is the growing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies. AI-enabled robots can monitor welding processes in real time, detect defects, and automatically adjust parameters to optimize quality, reduce rework, and minimize material waste. Leading manufacturers are incorporating AI-driven predictive maintenance, adaptive welding, and vision-based defect detection to enhance efficiency and reliability.
- In March 2024, Kane Robotics unveiled its GRIT vision system for cobots, featuring AI-powered visual sensors that replicate the human eye. The system enables real-time assessment of uneven surfaces, allowing cobots to make precise adjustments in sanding, grinding, and finishing operations, improving efficiency and accuracy in robotic weld grinding applications.
How is increasing automation across manufacturing industries influencing demand for robotic welding systems?
The growing shift toward automation in manufacturing is significantly increasing demand for robotic welding systems. Expanding production of automobiles, aerospace components, and heavy machinery is encouraging manufacturers to adopt robotic welding systems that can deliver precise, consistent, and high-quality welds while minimizing human error and labor costs. Rising focus on operational efficiency, production consistency, and safety, is further accelerating the adoption of advanced robotic welding technologies.
- In November 2024, LE Robotics (Loyalty Robotics Welding Systems) introduced its latest automated welding and cutting solutions, showcasing enhanced productivity, precision, and operational efficiency for industrial manufacturing at a global scale.
How do high capital investment and system complexity affect adoption among buyers?
A key challenge impeding the growth of the robotic welding market is the high capital investment required for system installation, programming, and integration. Deploying advanced robotic welding systems demands significant upfront expenditure on hardware, software, sensors, and specialized maintenance, making adoption difficult for small and medium-sized buyers.
Additionally, the shortage of skilled technicians capable of operating and maintaining these complex systems further restricts large-scale implementation across emerging markets.
To address this challenge, market players are focusing on developing cost-efficient and modular robotic welding systems that require minimal setup and training. Manufacturers are also introducing leasing models, automation-as-a-service solutions, and simplified user interfaces to lower adoption barriers and enhance accessibility for small and mid-sized enterprises.
How is the integration of collaborative robots (cobots) influencing manufacturing processes and safety?
The growing integration of collaborative robots (cobots) is reshaping manufacturing by enabling safer, more flexible, and highly efficient welding operations. Designed to work alongside human operators, cobots allow flexible production lines, quick reconfiguration, and greater accessibility for small and mid-sized manufacturers.
When combined with AI-driven control systems, these robots enhance weld precision, real-time decision-making, and process optimization. This convergence of robotics and artificial intelligence is accelerating adoption across automotive, aerospace, and general manufacturing sectors, driving higher efficiency and improved production outcomes.
- In September 2025, Universal Robots (UR), a provider of collaborative robotics solutions, announced plans to showcase a new cobot at FABTECH 2025 in Chicago. The robot is engineered to address complex welding challenges, offering enhanced reach, stability, and precision to advance automation in fabrication processes.
Robotic Welding Market Report Snapshot
|
Segmentation
|
Details
|
|
By Type
|
Arc Welding, Spot Welding, Laser Welding, TIG and MIG Welding, Others
|
|
By Payload Capacity
|
Up to 50 Kg, 50–150 Kg, Above 150 Kg
|
|
By End-Use Industry
|
Automotive & Transportation, Electrical & Electronics, Aerospace & Defense, Construction & Heavy Engineering, Others
|
|
By Region
|
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico
|
|
Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe
|
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific
|
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, U.A.E., Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa
|
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America
|
Market Segmentation:
- By Type (Arc Welding, Spot Welding, Laser Welding, TIG and MIG Welding, and Others): The arc welding segment earned USD 4.13 billion in 2024 due to its widespread adoption in automotive and heavy machinery manufacturing, offering high efficiency and consistent weld quality for large-scale production.
- By Payload Capacity (Up to 50 Kg, 50–150 Kg, and Above 150 Kg): The segment covering up to 50 kg equipment held 44.34% of the market in 2024, driven by its suitability for small- to medium-sized components and ease of integration in compact manufacturing lines.
- By End-Use Industry (Automotive & Transportation, Electrical & Electronics, Aerospace & Defense, and Construction & Heavy Engineering): The automotive & transportation segment is projected to reach USD 10.22 billion by 2032, owing to the increasing adoption of robotic welding for high-volume vehicle production and the need for consistent, high-quality welds.
What is the regional analysis of the global robotic welding market?
Based on region, the market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America.
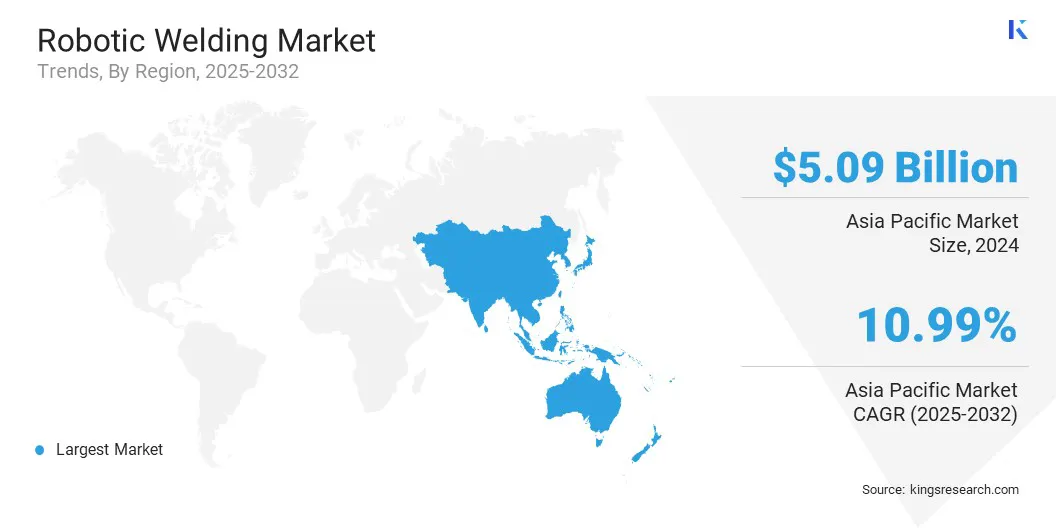
Asia Pacific robotic welding market share stood around 52.12% in 2024 in the global market, with a valuation of USD 5.09 billion. This dominance is driven by strong manufacturing growth across China, Japan, South Korea, and India. Rising labor costs, automation initiatives, and demand for high-precision production are accelerating adoption across automotive, electronics, and heavy machinery sectors.
Manufacturers are increasingly investing in advanced robotic welding methods that shorten cycle times, minimize defects, and enable complex, high-precision applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy engineering. The shift toward customized, high-performance manufacturing is accelerating the development of next-generation robotic welding solutions designed to meet evolving industrial demands.
- In March 2024, Yaskawa Electric and Toyota Motor Corporation, unveiled a new robotic welding method called Sequence Freezing Arc-Welding (SFA) in Japan. The technology was first applied to protective roll cages for racing cars, cutting production time from two to three weeks to just two to three days.
North America is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.36% over the forecast period. The North American robotic welding industry is expanding due to a high demand from the automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment segments. Efforts to reshore manufacturing operations and overcome skilled labor shortages are accelerating the adoption of automated welding solutions.
Manufacturers are integrating AI-enabled robotic systems capable of adaptive welding, predictive maintenance, and improved quality consistency across diverse production lines. Continuous advancements in vision systems, motion control, and human–robot collaboration are also improving operational efficiency and precision.
- In July 2025, Yaskawa America, Inc. announced plans to build a state-of-the-art robotic manufacturing facility at its new campus in Franklin, Wisconsin. This strategic initiative aims to expand production capabilities and strengthen Yaskawa’s presence in the North American market.
Regulatory Frameworks
- Globally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides global guidance on robotic welding systems, including safety, performance, and interoperability standards. Some other major authorities overseeing the use of robotic welders are as follows:
- In the U.S., robotic welding systems and industrial automation are overseen by Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), which sets safety standards for robotic operations, workplace integration, and operator training.
- In the EU, robotic welding and industrial automation are regulated under CE marking requirements and the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) for compliance with safety, health, and environmental standards.
- In APAC, China enforces safety and certification regulations through the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) and GB/T standards for industrial robots.
Competitive Landscape
Leading players in the robotic welding industry are focusing on innovation, portfolio expansions, and collaborative strategies to meet the rising demand for high-precision, automated manufacturing solutions. Companies are developing advanced robotic systems with AI-driven process optimization, real-time monitoring, and multi-axis functionalities to improve weld quality, reduce cycle times, and support complex applications.
Additionally, manufacturers are expanding regional production and service facilities, offering training programs for operators, and collaborating with system integrators to enhance accessibility, streamline deployment, and drive wider adoption across automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery industries.
- In September 2025, Miller Electric Mfg. LLC, a leading global manufacturer of Miller® brand arc welding equipment, introduced the XMT 400 multiprocess welder at FABTECH. The launch marked the latest addition to the company’s well-established XMT product line, designed to meet the needs of modern welding professionals seeking versatility, performance, and reliability in a single system.
Key Companies in Robotic Welding Market:
- ABB
- Fanuc Corporation
- Yaskawa America, Inc.
- KUKA SE & Co. KGaA
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Comau S.p.A.
- DENSO Robotics
- Nachi-fujikoshi corp.
- Panasonic Connect Co., Ltd.
- The Lincoln Electric Company
- Illinois Tool Works Inc.
- CLOOS Welding Technology GmbH
- Fronius International GmbH
- OTC Daihen Inc.
Recent Developments
- In November 2024, FANUC introduced the M-950iA industrial robot for heavy-duty welding operations. Its serial-link structure provides a wide range of motion, offering flexibility for tight workspaces and large-scale industrial fabrication. The introduction of the M-950iA is expected to enhance automation efficiency, improve weld precision, and reduce cycle times in high-load manufacturing environments.


