Market Definition
The market comprises materials and catalytic systems based on platinum group metals such as platinum, palladium, rhodium, and iridium that accelerate chemical reactions, while remaining unconsumed throughout the catalytic process. These catalysts enable high reaction efficiency, selectivity, and stability across critical industrial processes.
Its applications span automotive emission control, petroleum refining, chemical synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and clean energy systems, including fuel cells and hydrogen production, supporting regulatory compliance, process optimization, and sustainable manufacturing.
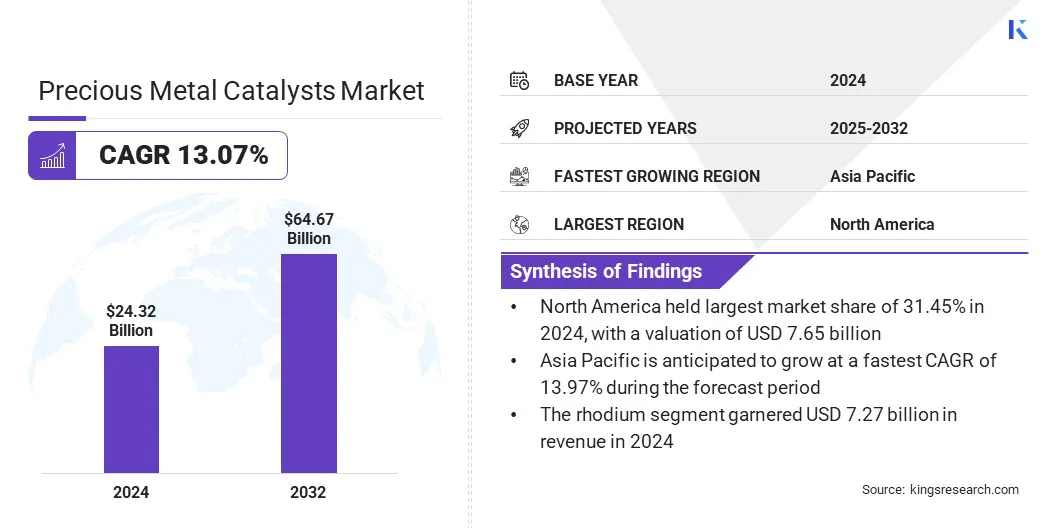
The global precious metal catalysts market size was valued at USD 24.32 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 27.37 billion in 2026 to USD 64.37 billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 13.07% during the forecast period.
This growth is driven by evolving vehicular emission regulations, rising adoption of advanced aftertreatment systems, and increasing use of platinum group metal catalysts to improve conversion efficiency and durability in exhaust control applications.
Key Market Highlights:
- The precious metal catalysts industry size was recorded at USD 24.32 billion in 2025.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.07% from 2026 to 2033.
- North America held a share of 31.45% in 2025, valued at USD 7.65 billion.
- The rhodium segment garnered USD 7.27 billion in revenue in 2025.
- The powder segment is expected to reach USD 8.08 billion by 2033.
- The petrochemicals segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of 13.48% over the forecast period.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 13.97% through the projection period.
Major companies operating in the precious metal catalysts market are ALS LIMITED, Alfa Chemistry, American Elements, BASF SE, Catalytic Products International, CHIMET, Sabin Metal Corporation, Clariant, Honeywell International Inc., Evonik Industries AG, Umicore, Heraeus Precious Metals, Johnson Matthey, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., and N.E. CHEMCAT.
Increasing use of precious metal catalysts in pharmaceutical synthesis reflects the growing reliance on platinum group metals to achieve high selectivity, reaction control, and yield consistency in complex drug manufacturing processes. These catalysts support critical steps such as hydrogenation, oxidation, and carbon–carbon coupling, enabling efficient synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Demand continues to rise due to stringent purity standards, shorter development timelines, and expanding biologics and specialty drug pipelines. Market participants are focusing on process optimization and cost efficiency, leading to the introduction of new catalysts to enhance scalability and regulatory compliance.
- In October 2025, Evonik launched the Noblyst F catalyst portfolio for flow applications, expanding its precious metal catalyst offerings. The portfolio features commercially available carbon-based catalysts in two particle sizes. Ongoing development focuses on additional support materials, sizes, and shapes to align catalyst performance with specific application requirements and process conditions.
The expansion of green hydrogen projects is increasing reliance on advanced catalytic materials that maintain high efficiency under demanding operating conditions. Electrolyzers and fuel cells require materials capable of accelerating reaction rates while maintaining long-term stability and minimal energy loss.
Platinum group metal-based catalysts are preferred due to their superior electrochemical properties. Growing investments in large-scale hydrogen infrastructure and stricter performance standards are prompting developers to adopt catalysts that support higher output, extended lifecycles, and consistent operational reliability.
- In May 2025, hte and Heraeus Precious Metals entered into an R&D service agreement to screen advanced materials for catalytic ammonia cracking to produce hydrogen. The collaboration utilized hte’s high-throughput system to evaluate catalyst performance and identify optimal formulations suitable for scalable and commercially viable hydrogen production applications.
Concerns pertaining to supply chain dependence on limited mining regions remain a significant challenge due to the geographic concentration of platinum group metal reserves. Supply disruptions, geopolitical risks, and regulatory uncertainties increase price volatility and procurement risks for catalyst manufacturers.
Heavy reliance on a few producing countries constrains supply flexibility and complicates long-term capacity planning. These factors impact cost structures, contract stability, and investment decisions across automotive, chemical, and energy sectors that depend on consistent catalyst availability.
To address this challenge, industry participants are diversifying sourcing strategies, increasing recycled metal utilization, forming long-term supply agreements, and investing in alternative catalyst formulations to reduce reliance on geographically concentrated mining regions.
The market is influenced by a growing focus on catalyst recycling and precious metal recovery to address cost pressures and supply constraints. High price volatility of platinum group metals prompts manufacturers and end users to recover valuable metals from end-of-life catalysts Recycling improves material availability, reduces dependence on primary mining, and aligns with sustainability objectives across industries.
Advances in recovery technologies and closed-loop supply models further boost adoption. These efforts enhance resource efficiency and long-term supply security through systematic precious metal recovery.
- In October 2025, Gannon & Scott signed a definitive agreement to join Metalor Technologies, part of TANAKA. The combination expands refining across all precious metals, strengthens access to high-purity materials, and integrates advanced analytical and R&D capabilities through Metalor’s global laboratory network.
|
Segmentation
|
Details
|
|
By Metal
|
Palladium, Platinum, Rhodium, Iridium, Ruthenium, Others
|
|
By Form
|
Powder, Pellet, Extrudate and Honeycomb, Wash coated Monolith
|
|
By Application
|
Automotive, Petrochemicals, Pharmaceutical, Electronics & Semiconductor, Others
|
|
By Region
|
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico
|
|
Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe
|
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific
|
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, U.A.E., Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa
|
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America
|
Market Segmentation
- By Metal (Palladium, Platinum, Rhodium, Iridium, Ruthenium, Others): The rhodium segment generated a revenue of USD 7.27 billion in 2025, mainly due to strong automotive catalyst demand, stringent emission norms, limited supply, and critical role in nitrogen oxide reduction.
- By Form (Powder, Pellet, Extrudate and Honeycomb, and Wash coated Monolith): The pellet segment is poised to record a CAGR of 13.24% through the forecast period, propelled by high surface area, efficient mass transfer, durability, and suitability for large-scale industrial reactors.
- By Application (Automotive, Petrochemicals, Pharmaceutical, Electronics & Semiconductor, and Others): The automotive segment is estimated to hold a share of 26.26% by 2033, fueled by stricter emission regulations, rising vehicle production, electrification trends, and rising demand for exhaust aftertreatment catalysts.
- Based on region, the global precious metal catalysts market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America.
What is the market scenario in North America and Asia Pacific region?
The North America precious metal catalysts market accounted for a share of 31.45% in 2025, valued at USD 7.65 billion. The region demonstrates high adoption of advanced catalyst technologies due to stringent environmental regulations and continuous upgrades in industrial processing standards. This dominance is reinforced by strong demand from automotive emission control, petroleum refining, and specialty chemical manufacturing.
Mature refining infrastructure and consistent investments in clean energy systems further sustain demand for platinum group metal catalysts. A strong presence of pharmaceutical manufacturing and chemical synthesis activities also contributes to steady consumption. Additionally, well-established recycling and recovery ecosystems enhance material availability, stabilizing supply chains and fostering regional market expansion.
- In May 2025, Umicore announced plans to expand homogeneous catalyst production at its Catoosa, Oklahoma facility to secure multi-ton supply from Europe and the U.S. for long-term specialty chemicals partnerships. The expansion supports fine chemicals, functional materials, polymers, and pharmaceuticals, while its advanced technologies lower energy use, reduce waste, and decrease carbon intensity across global manufacturing operations and compliance.
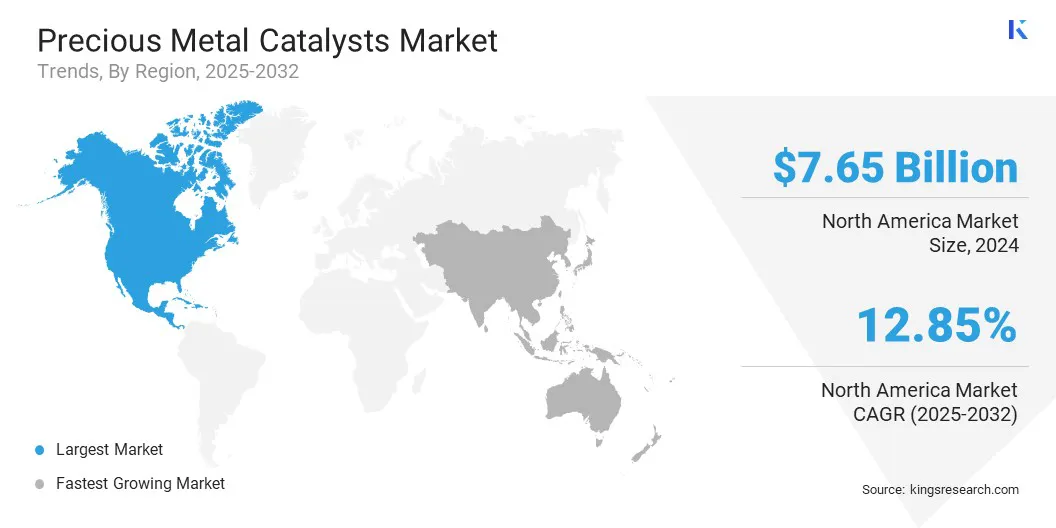
The Asia-Pacific precious metal catalysts industry is projected to register a CAGR of 13.97% over the forecast period. This growth is largely attributed to rapid industrial expansion and increasing demand across automotive, refining, and chemical processing sectors. Accelerated capacity additions in petrochemicals and the rising adoption of emission control technologies lead to widespread catalyst consumption.
Growth in pharmaceutical manufacturing and fine chemical production further strengthens demand for high-performance catalysts. Expanding investments in clean energy technologies, including hydrogen and fuel cell systems, increase reliance on platinum and iridium-based catalysts. The region’s cost-competitive manufacturing environment and expanding downstream industries support sustained volume growth and long-term market expansion.
Regulatory Frameworks
- In the U.S., the Clean Air Act (CAA) regulates automotive and industrial emissions. It mandates the use of advanced emission control technologies, highlighting the need for precious metal catalysts in exhaust aftertreatment and industrial pollution control systems.
- In the European Union, the REACH Regulation (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) governs chemical substances used in manufacturing. It controls catalyst composition, handling, and lifecycle management, influencing formulation, recycling, and compliance strategies for precious metal catalysts.
- In China, the China VI Emission Standards regulate vehicle exhaust emissions. They enforce stricter limits on nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, accelerating the adoption of rhodium, platinum, and palladium-based catalysts in automotive applications.
- In Japan, the Air Pollution Control Act oversees industrial and vehicular emission levels. It promotes deployment of high-efficiency catalytic systems, reinforcing the importance of precious metal catalysts across refining and transportation sectors.
- In India, the Bharat Stage VI (BS VI) Emission Norms control vehicular emissions. They mandate advanced catalytic converters, which leads to a substantial increase in the consumption of platinum group metal catalysts in the automotive segment.
- In South Africa, the Mineral and Petroleum Resources Development Act (MPRDA) governs the mining and processing of precious metals. It directly impacts raw material availability, pricing, and supply stability of precious metal catalysts.
Competitive Landscape
Key participants operating in the precious metal catalysts industry are prioritizing capacity expansion to address the rising demand across automotive, chemical, and energy-related applications. They are investing in advanced catalyst formulations to improve activity, selectivity, and thermal stability under demanding operating conditions. Strategic focus remains on strengthening recycling and precious metal recovery capabilities to manage raw material constraints and price volatility.
Several players are entering long-term supply agreements across industrial value chains to secure consistent feedstock availability. Increased allocation toward research and development supports process optimization and adaptation to evolving regulatory standards. Collaborations, technology partnerships, and portfolio diversification across end-use industries remain central actions to maintain competitive positioning.
- In January 2025, Mattiq announced a strategic partnership with Heraeus Precious Metals to develop and commercialize advanced electrocatalyst materials for green hydrogen production. The collaboration focuses on engineering low-iridium catalysts for PEM water electrolyzers, reducing reliance on critical raw materials while supporting scalable, zero-carbon hydrogen generation and future electrochemical technology development.
Key Companies in Precious Metal Catalysts Market:
- ALS LIMITED
- Alfa Chemistry
- American Elements
- BASF SE
- Catalytic Products International
- CHIMET
- Sabin Metal Corporation
- Clariant
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Evonik Industries AG
- Umicore
- Heraeus Precious Metals
- Johnson Matthey
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- E. CHEMCAT
Recent Developments (Agreements)
- In November 2025, BASF Environmental Catalyst and Metal Solutions (ECMS) commissioned a green hydrogen and fuel cell component manufacturing facility developed with Trigona Fuel Cell Components GmbH and Grundstücksverwaltung Rheinufer GmbH & Co. KG. The plant produces low-PGM-loaded CCMs for PEM electrolysis and fuel cells, supporting gigawatt-scale commercial deployment and advancing circular hydrogen solutions globally.
- In May 2025, Umicore announced an additional advanced production facility at its Catoosa site in the U.S., supported by a double-digit million investment and long-term contracts with specialty chemical companies. Construction begins in 2025, targeting homogeneous catalyst production by early 2027, strengthening multi-ton Grubbs Catalyst manufacturing capabilities and reinforcing industrial-scale adoption.
- In October 2024, The Royal Mint’s Precious Metals Recovery facility deployed Rockwell Automation’s PlantPAx DCS (distributed control system) to manage gold extraction operations. This implementation validated technical scalability, supported progress toward its 4,000-ton per annum target, and is accompanied by ongoing discussions on recovered material utilization and technology expansion.


