Genetic Testing Market Size
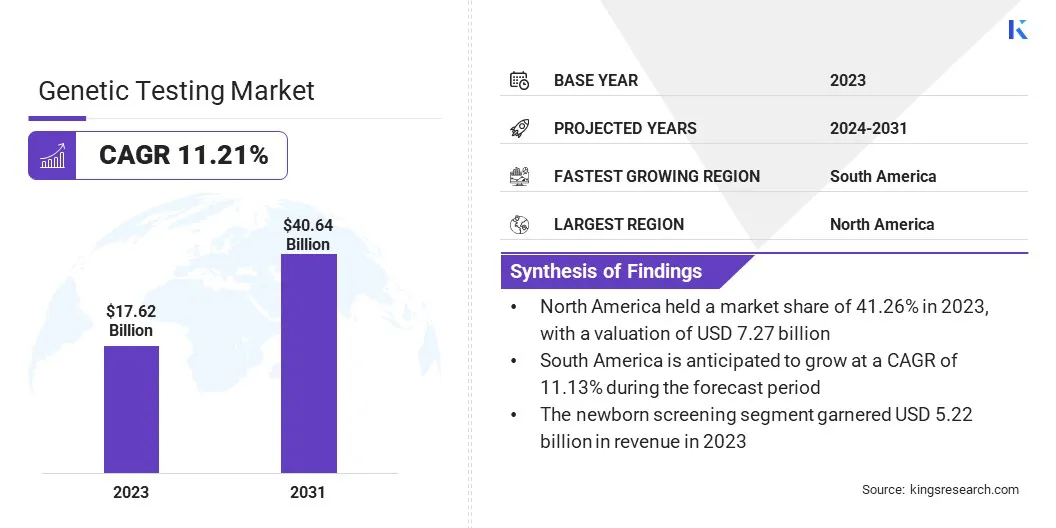
The global Genetic Testing Market size was valued at USD 17.62 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 40.64 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 11.21% from 2024 to 2031. In the scope of work, the report includes products offered by companies such as Abbott Laboratories, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Illumina Inc., Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Roche), Quest Diagnostics, Myriad Genetics, Inc., PerkinElmer Inc., BGI Group, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Exact Sciences Corporation and Others. The growth of the market is driven by technological advancements, the increasing prevalence of genetic disorders, and the growing trend of personalized medicine. Advancements in genomics technologies, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and microarray-based testing, have significantly reduced costs and improved testing accuracy.
Geographically, North America and Europe are leading the market due to well-established healthcare infrastructure, favorable reimbursement policies, and high adoption rates of advanced medical technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth in the foreseeable future, attributed to rising healthcare investments, increasing awareness about genetic testing, and growing partnerships between industry players and local healthcare providers.
The market is anticipated to continue its upward trajectory over the forecast period. Increasing R&D investments, expanding applications in non-clinical sectors such as ancestry testing, and the emergence of novel technologies viz., CRISPR-based testing contribute to this optimistic outlook.
Genetic testing involves analyzing an individual's DNA to identify variations, mutations, or abnormalities that may be linked to inherited disorders, disease risk factors, or drug responses. Key applications of genetic testing include diagnostic testing to confirm or rule out suspected genetic conditions, predictive and presymptomatic testing to assess disease risk before symptoms appear, carrier testing to determine if individuals carry a genetic mutation that could be passed on to their children, pharmacogenomic testing to guide personalized treatment plans based on genetic factors, and prenatal testing to screen for genetic conditions in unborn babies.
Analyst’s Review
The genetic testing market reflects a dynamic landscape marked by rapid technological advancements and increasing demand for personalized healthcare solutions. Market stakeholders, including major companies, startups, and research institutions, are strategically focusing on enhancing testing accuracy, expanding test offerings for diverse applications such as oncology, rare diseases, and pharmacogenomics, and improving accessibility through cost-effective solutions and telemedicine integration.
Collaborations between industry players and healthcare providers are fostering data-driven approaches, leveraging AI and big data analytics to offer more precise diagnostics and treatment recommendations. The market outlook is positively influenced by driven by continued innovation in genomics technologies, rising investments in genomic research, expanding adoption in emerging markets, and the integration of genetic testing into broader healthcare ecosystems for comprehensive patient care.
Genetic Testing Market Growth Factors
The advancement in disease treatment is a critical factor driving the growth of the genetic testing market, as it contributes to the expansion of personalized medicine and positively influences patient outcomes. Understanding one's genetic variants can guide treatment protocols, such as in the case of breast cancer where genetic testing can inform decisions regarding chemotherapy. The ability to tailor treatment based on genetic test results improves efficacy while reducing the need for unnecessary treatments and mitigating associated side effects.
Moreover, genetic testing can alleviate stress by providing clarity about disease risks or lack thereof, relieving individuals from the anxiety of uncertain health outcomes. These stress-relieving attribute further underscores the importance of genetic testing in promoting holistic healthcare management and enhancing overall patient well-being, which is contributing to the market's continued growth.
Moreover, the expansion of genetic testing applications beyond clinical diagnostics into non-clinical settings is a key factor fueling market growth. In addition to diagnosing diseases, genetic testing plays a crucial role in ancestry tracing, lifestyle management, and forensic identification, attracting a broader customer base and expanding market growth opportunities. Ancestry testing, in particular, has gained immense popularity among consumers interested in uncovering their genetic heritage and understanding inherited traits.
Additionally, genetic insights into lifestyle factors such as nutrition metabolism or exercise responses aid in personalized wellness strategies, thereby driving demand from health-conscious individuals. The integration of genetic testing into non-medical domains diversifies revenue streams for genetic testing companies, thereby aiding overall market growth by reaching a wider audience with varied needs and interests.
However, the genetic testing market faces several challenges that impact its growth and widespread adoption. The misconception that a negative genetic test result guarantees immunity from disease can lead to a false sense of security, as other environmental and lifestyle factors also contribute to disease development. This misunderstanding can hinder market growth by dampening the perceived value of genetic testing. Conversely, positive test results can induce unnecessary stress and anxiety, especially when dealing with uncertain outcomes or variants of unknown significance (VUS). This psychological burden may deter individuals from seeking genetic testing, thereby impacting market expansion.
Furthermore, the high cost of genetic testing and privacy concerns regarding data ownership and access pose additional barriers to widespread adoption. Ensuring accurate interpretation of results through qualified genetic counseling is crucial to addressing these challenges and fostering trust in genetic testing technologies.
Genetic Testing Market Trends
The field of genetic testing is undergoing transformative changes, driven by technological advancements and evolving healthcare needs. A major trend fueling industry growth is the acceleration of testing processes, wherein results are expected within minutes to hours, thereby enhancing its utility in acute care scenarios and pharmacogenetics.
Furthermore, the shift toward patient-centric testing plays a crucial role, as individuals can collect samples at home using simple devices or opt for point-of-care testing in clinics. Serial testing, which allows continuous monitoring of genetic changes over time, is becoming routine, and aids in disease surveillance and treatment assessment. Genetic testing serves various purposes from providing information to being actionable, guiding clinical management throughout different healthcare stages.
Moreover, the increasing democratization of genetic testing, supported by reliable genetic counseling services, has made it accessible to general practitioners and diverse healthcare professionals. Additionally, the expansion of testing to include RNA and epigenetic analyses, in addition to DNA, promises deeper insights into patient health and treatment responses, driving further advancements in personalized medicine.
Segmentation Analysis
The global genetic testing market is segmented based on purpose, type, technology, disease, sampling method, and geography.
By Purpose
Based on purpose, the market is bifurcated into clinical and research. The clinical segment accrued the largest market share of 90.12% in 2023 due to the increased affordability of large-scale genetic testing. A 2022 article, published by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), highlights the cost-effectiveness of recent advancements in genetic testing technologies. This affordability has encouraged more healthcare providers and patients to opt for clinical genetic testing, leading to a significant rise in its utilization. With clinical genetic testing offering insights into disease risk, diagnosis, treatment selection, and personalized medicine, its dominance reflects the growing importance and acceptance of genetic testing in mainstream healthcare practices.
By Type
Based on type, the market is segmented into diagnostic testing, presymptomatic or predictive testing, carrier testing, pharmacogenetics, prenatal testing, newborn screening, and preimplantation testing. The newborn screening segment is poised to reach a significant valuation of USD 5.22 billion by 2031 due to its widespread adoption and critical role in early disease detection. Over 95% of newborns in the United States undergo mandatory newborn screening, totaling approximately 4 million babies screened annually. This extensive screening helps identify genetic disorders and metabolic conditions early in life, enabling prompt intervention and treatment. As global awareness increases and healthcare infrastructure continues to improve, the demand for comprehensive newborn screening programs is expected to rise, thereby driving the growth of the newborn screening market in the coming years.
By Technology
Based on Technology, the market is classified into chromosome studies, DNA studies, and biochemical genetic studies. The DNA studies segment is anticipated to secure the largest market share of 50.16% by 2031 due to the increasing adoption of DNA studies, in cancer diagnostics and treatment planning. The American Cancer Society highlights that while hereditary cancers constitute only 5-12% of all cancers, DNA studies play a crucial role in identifying individuals with heightened risk for specific cancers such as breast, ovarian, and colon cancers. With advancements in DNA studies and a growing emphasis on personalized medicine, DNA studies for cancer susceptibility and targeted therapies are expected to drive steady growth in the market over the forecast period.
Genetic Testing Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the global market is classified into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, MEA, and Latin America.

The North America Genetic Testing Market share stood around 41.26% in 2023 in the global market, with a valuation of USD 7.27 billion. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a US government agency, increased awareness about the benefits of genetic testing for disease identification and treatment, particularly among an aging population, has driven the demand for genetic testing in the region. Furthermore, as technological advancements continue to make genetic testing faster, more affordable, and accessible, healthcare systems may leverage it for early disease detection and risk assessment, thereby boosting market growth in North America.
Latin America is poised to witness notable growth in the genetic testing market, exhibiting a CAGR of 11.13% over the forecast period. Research published in the International Journal for Equity in Health highlights the necessity for increased specialist training and funding to enhance the utilization of exome and whole-genome sequencing for diagnosing rare diseases in Brazil.
- Additionally, a study by the NIH on BRCA1/2 testing in Latin America observed significant improvements in laboratory practices, including increased sample analysis capacity. These advancements indicate a growing infrastructure and readiness for expanded genetic testing services in the region, which is set to propel regional market growth.
Competitive Landscape
The genetic testing market report will provide valuable insight with an emphasis on the fragmented nature of the industry. Prominent players are focusing on several key business strategies such as partnerships, mergers and acquisitions, product innovations, and joint ventures to expand their product portfolio and increase their market shares across different regions. Manufacturers are adopting a range of strategic initiatives, including investments in R&D activities, the establishment of new manufacturing facilities, and supply chain optimization, to strengthen their market standing.
List of Key Companies in the Genetic Testing Market
Key Industry Developments
- April 2023 (Partnership Extension): Centogene extended its strategic partnership with Takeda to provide continued access to genetic testing for patients with lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs). This collaboration aimed to enhance diagnosis and treatment options for individuals affected by these rare genetic conditions, with a focus on personalized healthcare solutions and improved patient outcomes.
- March 2023 (Partnership): Invitae, a leading genetic testing company, partnered with Epic Systems Corporation to integrate genetic testing into electronic health records (EHRs) seamlessly. This collaboration aimed to streamline the genetic testing process, improve access to genetic information for healthcare providers, and enhance patient care through more informed decision-making.
The global Genetic Testing Market is segmented as:
By Purpose
By Type
- Diagnostic Testing
- Presymptomatic or Predictive Testing
- Carrier Testing
- Pharmacogenetics
- Prenatal Testing
- Newborn Screening
- Preimplantation Testing
By Technology
- Chromosome Studies
- DNA Studies
- Biochemical Genetic Studies
By Disease
- Cancer
- Alzheimer’s
- Thalassemia
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Huntington’s Disease
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Other Diseases
By Sampling Method
- Blood sample
- Cheek swab
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- France
- U.K.
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- North Africa
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America


