Market Definition
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is a modern cybersecurity model that eliminates the assumption of implicit trust across digital systems. It enforces continuous verification of users, devices, and applications before granting access, regardless of their network location.
Unlike perimeter-driven approaches, ZTA addresses the possibility of threats originating within and outside the enterprise environment. This framework applies identity-based security, network segmentation, restricted access privileges, and continuous monitoring, making it essential for safeguarding complex IT and cloud infrastructures.
The market encompasses technologies, solutions, and services that enable organizations to implement this security framework, including identity and access management (IAM), multi-factor authentication (MFA), secure access service edge (SASE), cloud security, endpoint security, and network micro-segmentation.
Zero Trust Architecture Market Overview
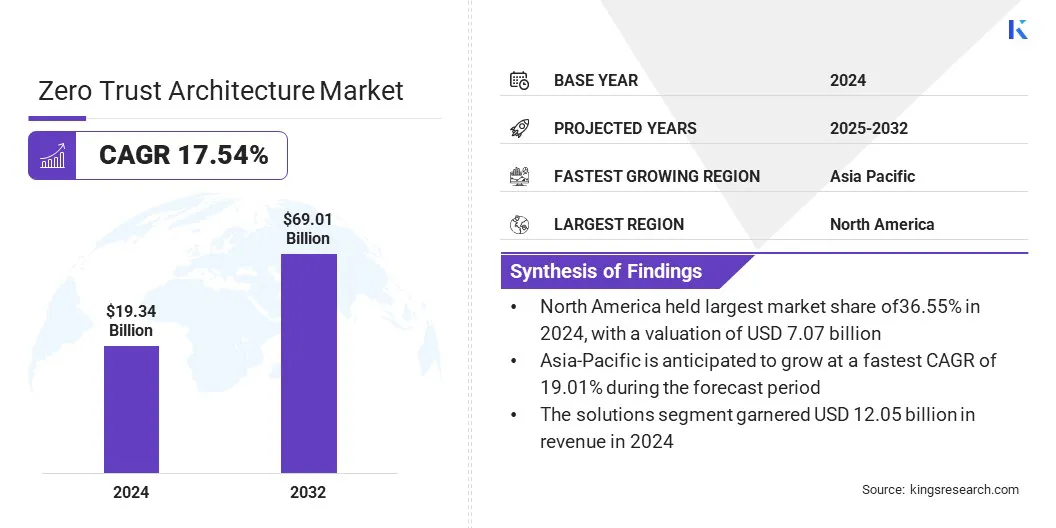
According to Kings Research, the global zero trust architecture market was valued at USD 19.34 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 22.26 billion in 2025 to USD 69.01 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 17.54% during the forecast period.
The Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) market is experiencing strong growth as organizations shift from traditional perimeter-based defenses to identity-centric security frameworks. Moreover, the rise in remote and hybrid work models, rapid cloud adoption, and the increasing frequency of sophisticated cyberattacks that bypass conventional controls is further driving the market.
Key Market Highlights:
- The zero trust architecture industry was recorded at USD 19.34 billion in 2024.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.54% from 2024 to 2032.
- North America held a market of 36.55% in 2024, with a valuation of USD 7.07 billion.
- The solutions segment garnered USD 12.05 billion in revenue in 2024.
- The cloud segment is expected to reach USD 33.62 billion by 2032.
- The large enterprises segment registered a market share of USD 57.32 billion in 2024.
- The healthcare & life sciences segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of 19.60% from 2024 to 2032.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 19.01% over the forecast period.
Major companies operating in the zero trust architecture market are Zscaler, Inc., Palo Alto Networks., Cisco Systems, Inc., Akamai Technologies, Fortinet, Inc., Check Point Software Technologies Ltd., Cloudflare, Inc., IBM Corporation, Netskope, Cato Networks Ltd, Versa Networks, Inc., ARYAKA NETWORKS, INC., iboss, Appgate, and Microsoft.
The increasing need for continuous verification and least-privilege access is driving the demand for zero trust architecture in enterprises with complex security requirements. Zero trust is enabling organizations to strengthen identity control, protect sensitive data, and reduce the risk of lateral movement within networks.
Integration with secure access service edge (SASE) frameworks and AI-driven threat analytics is creating opportunities for more adaptive and proactive defenses, supporting real-time risk mitigation across distributed environments. National cybersecurity mandates are further accelerating adoption, with governments positioning Zero Trust as a foundational security model.
Enterprises are increasingly implementing Zero Trust solutions to improve compliance, modernize legacy security infrastructures, and ensure consistent protection across cloud, on-premise, and hybrid systems, thereby driving the market growth.
- In February 2025, Veeam Software expanded its partnership with Microsoft, which included a strategic equity investment from Microsoft. The collaboration focuses on developing AI-powered solutions aimed at enhancing data protection, accelerating recovery processes, and enabling enterprises to extract greater value from their data assets.
Market Driver
Rising Cybersecurity Threats
The rising incidence of sophisticated cyberattacks and data breaches is driving strong demand for Zero Trust Architecture. Enterprises are facing escalating risks from ransomware, insider threats, and advanced persistent attacks, which have heightened the need for continuous authentication, identity validation, and least-privilege access controls.
Zero Trust frameworks address these requirements by enforcing micro-segmentation and real-time monitoring across users, devices, applications, and networks.
The increasing adoption of cloud services, hybrid work models, and IoT ecosystems is further increasing the demand for Zero Trust as organizations seek to secure distributed environments without compromising agility.
Regulatory mandates in sectors such as BFSI, healthcare, and government are also reinforcing adoption, making Zero Trust a critical foundation for modern cybersecurity strategies and a primary driver of market growth.
- In May 2024, Zscaler, Inc. entered into a partnership with Google to introduce a joint Zero Trust Architecture integrated with Chrome Enterprise. The collaboration combines Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) to provide secure, Zero Trust-based access to private applications across diverse devices and locations, with the advanced threat detection and data protection features of Chrome Enterprise Premium.
Market Challenge
Complexity of Integration with Legacy Systems and Policy Enforcement
A key challenge in the Zero Trust Architecture market is the complexity of integrating Zero Trust principles into existing IT environments with diverse legacy systems and siloed applications. Minor gaps in identity management or misconfigured access policies can reduce the effectiveness of the framework, leading to security blind spots and operational inefficiencies.
This complexity requires significant investment in skilled personnel and advanced integration tools, increasing the cost and time needed for full-scale adoption.
To address this challenge, vendors are developing more flexible Zero Trust solutions that support seamless interoperability across hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures. Enterprises are also deploying automation and AI-driven monitoring to simplify policy enforcement, reduce human error, and ensure consistent application of Zero Trust controls across distributed networks.
Market Trend
Integration of Zero Trust with Unified Cloud and Network Security
A key trend in the market is the growing convergence of Zero Trust frameworks with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and cloud-native security models. Enterprises are increasingly seeking unified solutions that combine identity-based access, network security, and real-time threat detection into a single platform.
This is driven by the shift toward hybrid and multi-cloud environments, where traditional perimeter defenses are insufficient. Organizations are also prioritizing simplified management and scalability, enabling IT teams to enforce consistent policies across distributed applications and devices.
Vendors are responding by delivering integrated Zero Trust and SASE offerings that reduce complexity, enhance performance, and provide seamless user experiences without compromising security.
- In December 2023, Versa Networks, a global leader in AI/ML-powered Unified Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN), announced its selection to deliver SD-WAN, Zero Trust access, and Customer Edge Security Stack (CESS) capabilities for Thunderdome.
Zero Trust Architecture Market Report Snapshot
|
Segmentation
|
Details
|
|
By Component
|
Solutions, Services
|
|
By Deployment Mode
|
On-premises, Cloud
|
|
By Organization Size
|
Large Enterprises, Small & Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs)
|
|
By Industry Vertical
|
Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI), IT & Telecommunications, Government & Defense, Healthcare & Life Sciences, Others
|
|
By Region
|
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico
|
|
Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe
|
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific
|
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, U.A.E., Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa
|
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America
|
Market Segmentation:
- By Component (Solutions, Services): The solutions segment earned USD 12.05 billion in 2024 due to increasing adoption of advanced zero trust platforms to secure hybrid and cloud-based environments.
- By Deployment Mode (On-premises, Cloud): The on-premises segment held a market of 54.32% in 2024, due to strong demand from highly regulated industries that prioritize data sovereignty and internal security control.
- By Organization Size (Large Enterprises, Small & Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs): The large enterprises segment is projected to reach USD 36.78 billion by 2032, owing to the growing need for scalable Zero Trust frameworks to secure complex, multi-cloud infrastructures and global workforce operations.
- By Industry Vertical (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance, IT & Telecommunications, Government & Defense, Healthcare & Life Sciences, and Others): The IT & telecommunications is expected to hold 43.95% of the market share by 2032, due to rising demand for secure remote access, cloud-native applications, and protection against advanced cyber threats in highly connected networks.
Zero Trust Architecture Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the global market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America.
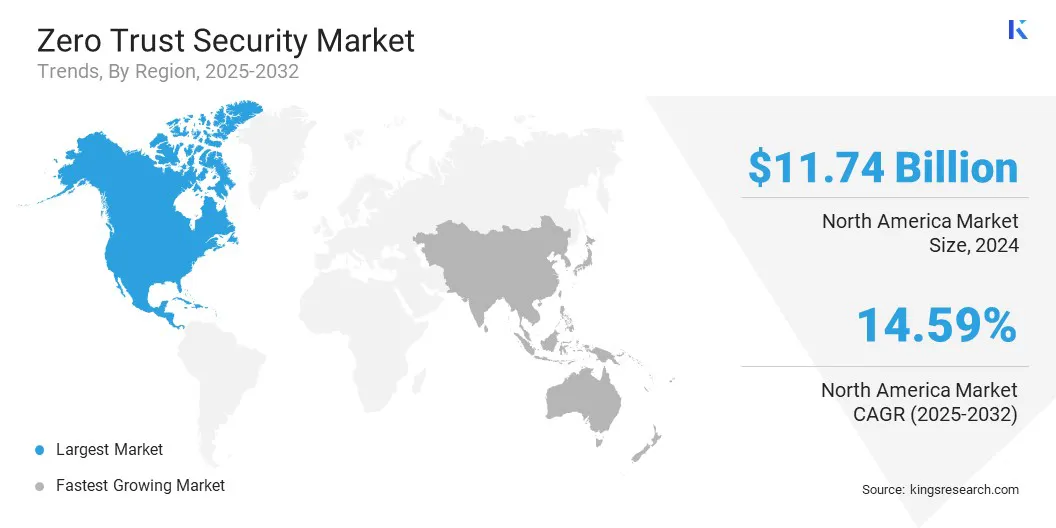
North America zero trust architecture market share stood at 36.55% in 2024 in the global market, with a valuation of USD 7.07 billion. The dominance is attributed to the growing threat landscape in the region, where ransomware, phishing, and other cyberattacks are prompting organizations to implement stricter identity-based security models.
Enterprises across sectors such as BFSI, healthcare, and government in this region are increasingly adopting Zero Trust due to stringent regulatory requirements and high-value data protection needs. Moreover, businesses in North America are investing heavily in AI-driven security and cloud-native Zero Trust platforms to simplify operations and ensure resilience in hybrid work environments.
- In May 2023, Zscaler announced a partnership with the Center for Internet Security (CIS) to support U.S. State, Local, Tribal, and Territorial (SLTT) government agencies. Through this collaboration, government agencies in the country will be able to leverage the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange platform to strengthen identity management, maintain operational control, and enforce security policies more effectively.
Asia-Pacific is poised for significant growth at a robust CAGR of 19.01% over the forecast period. The region’s enterprises are facing rising cybersecurity threats, particularly with the increase in remote work, e-commerce, and mobile-first business models.
Adoption is further encouraged by government-led initiatives in countries such as China, Japan, and India, where regulatory frameworks and national cybersecurity strategies are reinforcing the shift toward Zero Trust models.
Organizations across sectors, including BFSI, telecom, and manufacturing, are prioritizing investments in identity management, secure access, and micro-segmentation to safeguard distributed networks.
Moreover, the presence of a large SME base in Asia-Pacific is fueling demand for cost-effective and scalable Zero Trust solutions delivered through cloud platforms. This combination of regulatory momentum, digital adoption, and heightened threat exposure is positioning Asia-Pacific as a high-growth hub for Zero Trust deployment.
Regulatory Frameworks
- In the U.S., Zero Trust adoption is strongly influenced by Executive Order 14028 (2021), which mandates federal agencies to implement Zero Trust principles. Oversight is provided by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) through its Zero Trust Maturity Model and by the NIST SP 800-207 framework, which sets baseline standards for deployment across both public and private sectors.
- In the European Union, the region is governed by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the NIS2 Directive, both of which emphasize identity verification, data minimization, and secure access controls. Member states also align with the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) guidance, ensuring compliance and interoperability in cross-border data protection.
- Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan): China enforces strict cybersecurity requirements under its Cybersecurity Law and Data Security Law, requiring government approval for critical digital infrastructure protection. India’s National Cybersecurity Strategy emphasizes Zero Trust adoption for government and financial institutions, while Japan’s Cybersecurity Basic Act and related guidelines from the National Center of Incident Readiness and Strategy for Cybersecurity (NISC) encourage enterprises to deploy Zero Trust models, particularly in critical sectors.
- International Bodies: Organizations such as the OECD and World Economic Forum (WEF) actively promote Zero Trust best practices as part of global digital resilience initiatives. Meanwhile, the ISO/IEC 27001 standard and related frameworks provide international alignment on secure access, data governance, and identity protection.
Competitive Landscape
The global zero trust architecture market is characterized by a large number of participants, including established corporations and rising organizations. Major players in the market are pursuing strategies such as continuous product innovation, advanced R&D, and strategic partnerships to strengthen cybersecurity resilience across industries.
Market players are developing scalable Zero Trust solutions tailored for diverse enterprise environments to enhance identity protection, secure cloud migration, and reduce reliance on perimeter-based security models.
Top Companies in Zero Trust Architecture Market:
- Zscaler, Inc.
- Palo Alto Networks.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Akamai Technologies
- Fortinet, Inc.
- Check Point Software Technologies Ltd.
- Cloudflare, Inc.
- IBM Corporation
- Netskope
- Cato Networks Ltd
- Versa Networks, Inc.
- ARYAKA NETWORKS, INC.
- iboss
- Appgate
- Microsoft
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, Zscaler, Inc. introduced its Zero Trust Network Access solution, Zscaler Private Access for SAP, built on the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange platform. The service supports SAP customers with on-premise ERP workloads by simplifying cloud migration and minimizing associated risks, while eliminating the complexities and security gaps of traditional VPNs.
- In October 2024, Airtel Business collaborated with Zscaler Inc. to introduce Airtel Secure Digital Internet, the first fully managed solution based on Zero Trust Architecture. The offering is designed to provide enterprises with robust protection against evolving cyber threats.


