Market Definition
A vegetable seed is the reproductive unit of a vegetable plant that carries the genetic material necessary to produce the next generation of crops. It is the foundational input in horticulture, determining the plant’s growth, yield, nutritional quality, and resistance to pests and diseases. Vegetable seeds are broadly categorized into open-pollinated varieties (OPVs), hybrids (F1), and increasingly, genetically improved or biotechnologically enhanced seeds.
OPVs allow farmers to save seeds for future cultivation, whereas hybrids are developed through controlled cross-pollination to ensure desirable traits like uniformity, disease resistance, or higher yield. Vegetable seeds undergo stringent processes such as breeding, germination testing, cleaning, and sometimes coating or pelleting for better handling and protection.
They are essential in commercial agriculture, greenhouse cultivation, kitchen gardening, and urban farming. The quality of seeds directly influences productivity, making them one of the most critical inputs in modern agriculture and a key driver of global food security.
Vegetable Seed Market Overview
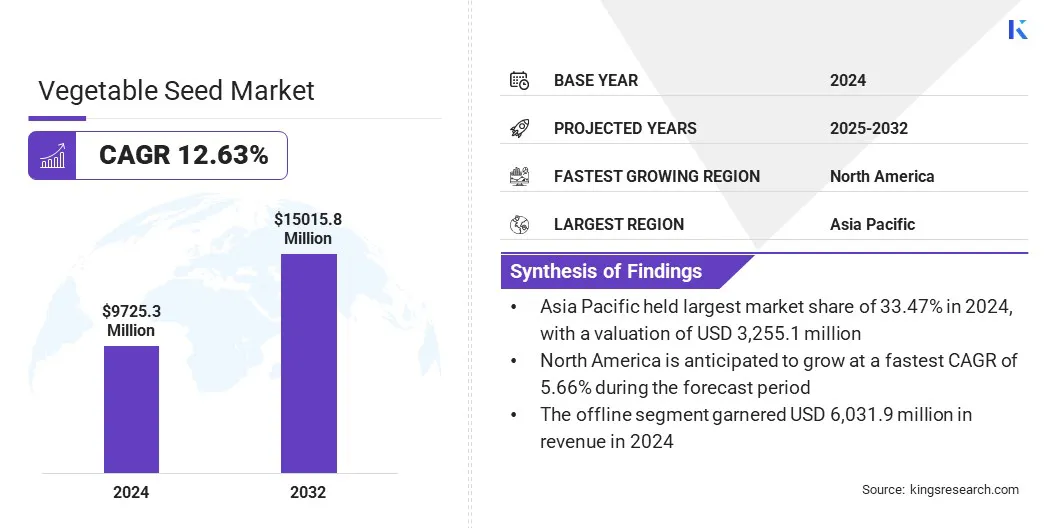
The global vegetable seed market size was valued at USD 9,725.3 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 10,240.7 million in 2025 to USD 15,015.8 million by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.53% during the forecast period.
Growing demand for organic and non-GMO vegetable seeds reflects consumer preference for healthier, chemical-free produce. This trend strengthens the market, driving innovation in sustainable and eco-friendly seed varieties.
Key Highlights
- The global vegetable seed industry was recorded at USD 9,725.3 million in 2024.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.53% from 2025 to 2032.
- Asia Pacific held a market share of 33.47% in 2024, valued at USD 3,255.1 million.
- The tomato segment garnered USD 1,532.8 million in revenue in 2024.
- The roots & bulbs segment is expected to reach USD 3,565.6 million by 2032.
- The organic segment is anticipated to witness fastest CAGR of 6.00% during the forecast period.
- The offline segment is predicted to hold the market of 60.75% in 2032.
- North America is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.66% through the projection period.
Major companies operating in the vegetable seed market are Bayer AG, Syngenta, BASF SE, SAKATA SEED CORPORATION, Corteva, Limagrain Group, Bejo Zaden B.V., Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel B.V., Enza Zaden, KNOWN-YOU SEED CO., LTD, UPL, TAKII & CO.,LTD., East-West Seed, KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA, Yuksel Seeds, and others.
 Advancements in technology are reshaping the vegetable seed industry by accelerating breeding processes and enhancing the genetic potential of crops. Tools such as CRISPR gene-editing, marker-assisted selection, and genomic sequencing allow seed developers to create varieties with improved yield, disease resistance, and adaptability to diverse climates.
Advancements in technology are reshaping the vegetable seed industry by accelerating breeding processes and enhancing the genetic potential of crops. Tools such as CRISPR gene-editing, marker-assisted selection, and genomic sequencing allow seed developers to create varieties with improved yield, disease resistance, and adaptability to diverse climates.
Digital phenotyping and AI-driven analytics further support breeders by shortening the breeding cycle and predicting crop performance under various conditions. These technological breakthroughs offer a significant opportunity for the vegetable seed market, enabling companies to deliver targeted, high-value seed varieties tailored to specific farmer requirements.
By integrating biotechnology, precision agriculture, and data-driven solutions, the market is positioned to revolutionize vegetable production, ensuring sustainable food supply and competitive growth in global agriculture.
Market Driver
Expansion of hybrid seed usage is accelerating the growth of the vegetable seed
The increasing use of hybrid seeds is a critical driver accelerating the growth of the vegetable seed industry. Hybrid seeds are developed through controlled cross-pollination, combining desirable traits from two parent lines to produce superior offspring. These seeds deliver higher yields, uniform size, better taste, and enhanced resistance to pests and diseases, making them highly attractive to commercial growers.
Farmers also benefit from improved shelf life and transportability of hybrid-grown vegetables, supporting supply chain efficiency. The expansion of hybrid seed usage addresses the global challenge of producing more food on limited arable land. As consumer demand for high-quality vegetables rises, seed companies continue investing heavily in hybrid breeding programs, consolidating hybrid seeds as the cornerstone of future market growth.
- In May 2025, East-West Seed inaugurated the 36-hectare Hortanova Research Center in San Juan, Batangas, advancing hybrid breeding, climate-resilient varieties, and farmer diversification to strengthen research capacity, delivers superior traits, and reinforces the company’s commitment to innovation and farmer productivity.
Market Challenge
Climate Change Poses Significant Challenges to the Market
Climate change poses a major challenge for the vegetable seed industry by disrupting growing conditions and reducing crop reliability. Rising temperatures, irregular rainfall, extended droughts, and the emergence of new pest and disease patterns put pressure on farmers to adapt.
Traditional varieties often fail to withstand such extremes, resulting in unstable yields and increased vulnerability of food systems. This challenge directly impacts the consistency of vegetable supply and profitability for growers.
To overcome it, seed companies are developing climate-resilient varieties with traits such as heat tolerance, drought resistance, and improved adaptability to changing agro-ecological zones. These innovations secure stable production in unpredictable environments and ensure that the market continues to thrive despite climatic disruptions.
- For instance, Spain experienced a decrease in the production of tomatoes by approximately 22% in February 2023 due to unpredictable weather conditions. This, in turn, resulted in surged prices for the same vegetable in the U.K. Such supply chain disruptions due to climate changes poses substantial challenges globally.
Market Trend
Rising adoption of protected cultivation and vertical farming
The rising adoption of protected cultivation and vertical farming is a key trend influencing the vegetable seed market. Protected systems, including greenhouses and polyhouses, create controlled environments that optimize water use, nutrient delivery, and pest management.
Vertical farming, leveraging hydroponics and LED-based artificial lighting, maximizes production in limited urban spaces. Both approaches demand specialized seed varieties capable of performing well under artificial conditions, such as compact growth, short maturity cycles, and disease resistance.
This trend supports year-round vegetable production which helps meet consumer demand for fresh, high-quality produce in urban markets. For the market, it creates opportunities to innovate with tailored varieties suited for indoor and vertical systems, driving long-term expansion.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), global vegetable production is anticipated to increase by 47% by 2050, emphasizing the pressing need for sustainable and efficient cultivation methods.
Vegetable Seed Market Report Snapshot
|
Segmentation
|
Details
|
|
By Type
|
Tomato, Onion, Carrot, Melon, Lettuce, Pepper, Broccoli, Cucumber, Cauliflower, and Others
|
|
By Crop Type
|
Solanaceae, Roots & Bulbs, Cucurbit, Brassica, and Others
|
|
By Form
|
Inorganic, and Organic
|
|
By Sales Channel
|
Offline, and Online
|
|
By Region
|
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico
|
|
Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe
|
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific
|
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, U.A.E., Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa
|
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America
|
Market Segmentation
- By Type (Tomato, Onion, Carrot, Melon, Lettuce, Pepper, Broccoli, Cucumber, Cauliflower, and Others): The tomato segment earned USD 2,596.5 million in 2024 due to high global consumption, demand for hybrids with disease resistance, and adoption in protected cultivation boosting yields and profitability.
- By Crop Type (Solanaceae, Roots & Bulbs, Cucurbit, Brassica, and Others): The solanaceae held 31.41% of the market in 2024, due to widespread cultivation of tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants, supported by strong commercial demand, hybrid advancements, and climate-resilient seed varieties.
- By Form (Inorganic, and Organic): The inorganic segment is projected to reach USD 8,073.8 million by 2032, owing to affordability, easier availability, longer shelf life, and suitability for large-scale farming compared to costlier organic seed alternatives.
- By Sales Channel (Offline, and Online): The online segment is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.97% over the forecast period owing to digital platforms offering convenience, broader access, competitive pricing, and direct farmer engagement.
Vegetable Seed Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America.
.webp) The Asia Pacific vegetable seed industry accounted for approximately 33.47% share in 2024, valued at USD 3,255.1 million, reflecting the region’s dominant role in global horticulture. This leadership is supported by extensive vegetable cultivation across China, India, and Southeast Asian countries, where farming remains a vital part of economic activity.
The Asia Pacific vegetable seed industry accounted for approximately 33.47% share in 2024, valued at USD 3,255.1 million, reflecting the region’s dominant role in global horticulture. This leadership is supported by extensive vegetable cultivation across China, India, and Southeast Asian countries, where farming remains a vital part of economic activity.
Strong government support programs, rising demand for hybrid and climate-resilient seeds, and growing adoption of protected cultivation practices contribute to the region’s high market valuation. Moreover, increasing consumer preference for fresh, nutrient-rich vegetables and rapid urbanization driving kitchen and urban gardening further stimulate seed demand.
Asia Pacific’s expanding population, combined with technological advancements in breeding and seed distribution, positions the region as a key growth engine for the global vegetable seed industry.
- For instance, in March 2023, according to the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) is actively fostering the development of new crop varieties, including vegetables, through its extensive network.
North America is projected to witness strong growth in the vegetable seed market, expanding at a CAGR of 5.66% over the forecast period. This momentum is fueled by advanced farming infrastructure, widespread adoption of greenhouse and hydroponic systems, and increasing demand for high-value crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and leafy greens.
Farmers in the region prefer hybrid and disease-resistant seeds to maximize productivity and minimize losses from pests and climate variability. Rising consumer demand for organic produce, coupled with health-focused diets, accelerates the adoption of premium vegetable seed varieties. In addition, technological innovation, precision agriculture, and partnerships between seed companies and research institutions are creating new opportunities.
- For instance, in 2022, according to USDA National Agricultural Statistics Service, the value of utilized production for vegetable crops was USD 16.5 billion, up 27% from the previous year.
Regulatory Frameworks
- In the European Union, the EU Seed Marketing Directives regulate the production and marketing of vegetable seeds. It ensures varietal registration, seed certification, and quality standards to maintain transparency, uniformity, and farmer confidence across member states.
- In the United States, the Federal Seed Act regulates the labeling and sale of vegetable seeds. It sets rules for truthful labeling, purity, and germination standards, ensuring farmers receive accurate information for planting decisions.
- In India, the Seeds Act, 1966 regulates the quality of vegetable seeds. It mandates minimum quality standards, certification, and testing, safeguarding farmers from spurious seeds and supporting the growth of the market.
- In China, the Seed Law of the People’s Republic of China regulates seed production and trading. It emphasizes variety protection, quality control, and intellectual property rights to strengthen innovation in the market.
- In Brazil, the National Seed and Seedling Law (Law No. 10,711/2003) regulates seed production, certification, and commercialization. It promotes high-quality seed supply and ensures credibility within the Brazilian market.
- In Japan, the Seed and Seedling Law regulates seed certification and distribution. It focuses on quality assurance, varietal protection, and labeling standards to support domestic vegetable farming and maintain market reliability.
- In Canada, the Seeds Act regulates import, export, and sale of vegetable seeds. It requires compliance with germination and varietal standards, ensuring quality and protecting farmers from fraudulent seed transactions.
Competitive Landscape
Key players in the vegetable seed industry are focusing on innovative breeding technologies, hybrid development, and biotechnology applications to strengthen their market presence. A major strategy includes investment in R&D programs to develop high-yielding, disease-resistant, and climate-resilient seed varieties.
Companies are also enhancing their portfolios by targeting specialized seeds for greenhouse, hydroponic, and vertical farming systems, reflecting the rising trend of protected cultivation. Strategic partnerships with agricultural research bodies and local distributors are helping firms expand reach in both mature and emerging markets.
Current growth is driven by the demand for premium, non-GMO, and organic-certified seeds, aligning with evolving consumer preferences. The winning imperatives for these players include continuous innovation, strengthening supply chains, leveraging digital platforms for seed distribution, and aligning with sustainability goals to secure long-term competitiveness.
- In July 2025, Sakata Seed Corporation announced the acquisition of Agritu Sementes Ltda, a Brazil-based onion seed specialist. With strong local roots in Santa Catarina, Agritu offers advanced seed technology, established sales channels, and market-recognized onion production, now operating as Sakata’s subsidiary.
Key Companies in Vegetable Seed Market:
- Bayer AG
- Syngenta
- BASF SE
- SAKATA SEED CORPORATION
- Corteva
- Limagrain Group
- Bejo Zaden B.V.
- Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel B.V.
- Enza Zaden
- KNOWN-YOU SEED CO., LTD
- UPL
- TAKII & CO.,LTD.
- East-West Seed
- KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA
- Yuksel Seeds
Recent Developments (M&A/Partnerships/Agreements/New Product Launch)
- In January 2025, Syngenta Vegetable Seeds and Apricus Seeds signed a global licensing agreement granting Syngenta exclusive access to Apricus’ advanced germplasm and breeding pipeline in watermelon, melon, and squash, strategically strengthening Syngenta’s cucurbits portfolio and enhancing its global vegetable seed capabilities.
- In April 2025, Source.ag, a leading AI solutions provider for vegetable growers, announced a partnership with Axia Vegetable Seeds, a specialist in high-yield hybrids. Axia will deploy Source.ag’s AI technologies in its Demo Greenhouse to enhance efficiency and optimize seed breeding operations.
- In October 2023, Sakata acquired Sana Seeds, a Dutch company specializing in high-quality cucumber varieties. Through its European subsidiary, Sakata aimed to accelerate cucumber research, strengthen its business in Europe, and enhance its global fruit vegetable portfolio. The acquisition fostered collaboration, expanded the product range, and leveraged Sana Seeds' expertise in the European "long type" cucumber segment, contributing to Sakata's commitment to sustainable agriculture and global nutrition improvement.
- In July 2023, Syngenta Vegetable Seeds successfully completed the acquisition of Feltrin Sementes, consolidating its standing in the market. The acquisition broadened Syngenta's portfolio, enabling the company to provide farmers with an extended range of high-quality vegetable seeds.
- In June 2023, BASF, Syngenta, and Arisa announced the completion of the first phase of the Multistak project in 2023 to develop innovative solutions for sustainable vegetable seed production, signifying progress in advancing agricultural technologies and practices for the benefit of the global vegetable seed industry.


.webp)