Fecal Occult Testing Market Size
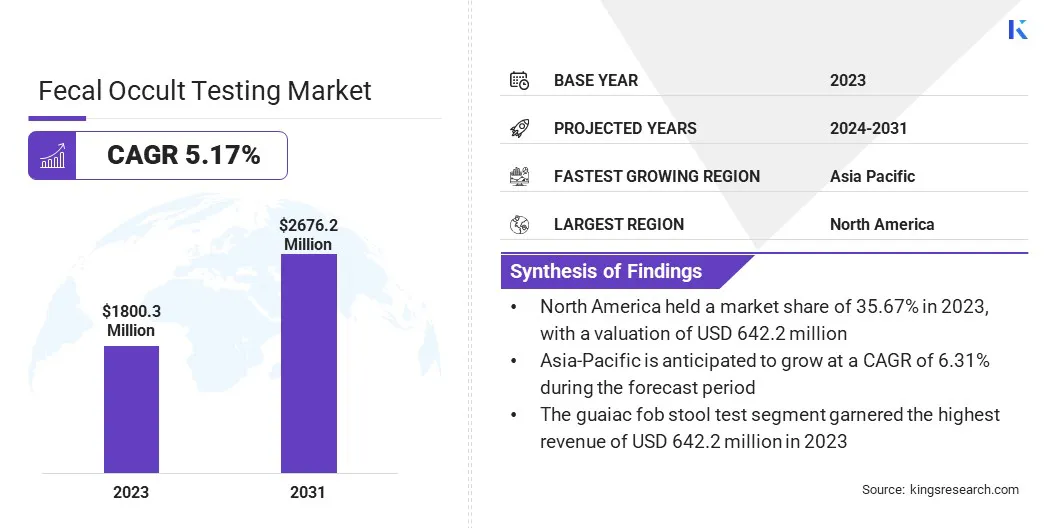
The global Fecal Occult Testing Market size was valued at USD 1,800.3 million in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 1,880.8 million in 2024 to USD 2,676.2 million by 2031, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.17% during the forecast period. In the scope of work, the report includes solutions offered by companies such as Abbott, HemoCue America (Danaher company), QuidelOrtho Corporation, Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc, Biohit Oyj, Polymedco, LLC., Quest Diagnostics, Randox Laboratories Ltd, New Day Diagnostics and others.
Fecal occult testing detects hidden blood in stool, which is crucial for the early detection of gastrointestinal disorders such as colorectal cancer. It involves analyzing stool samples for microscopic amounts of blood using chemical or immunological methods, aiding in timely medical intervention and improved patient outcomes.
Fecal occult testing plays a crucial role in colorectal cancer screening, offering non-invasive methods to detect microscopic traces of blood in stool samples, which is indicative of early-stage abnormalities. With colorectal cancer ranking among the most prevalent cancers globally, the fecal occult testing market is influenced by increasing incidences and the growing emphasis on preventive healthcare.
Advancements in test technologies, such as immunochemical tests (FIT), enhance accuracy and ease of use, further boosting market growth. Public health campaigns and government initiatives promoting screening programs contribute to higher adoption rates among at-risk populations,. This supports the expansion of the market by improving early diagnosis and treatment outcomes.
- The American Cancer Society estimates that 152,810 people in the U.S. will be diagnosed with colorectal cancer in 2024, and 53,010 will die from the disease.
Fecal occult testing, often referred to as fecal occult blood testing (FOBT), is a diagnostic procedure used to detect small amounts of blood in stool that are not visibly apparent. The presence of occult (hidden) blood can indicate various gastrointestinal conditions, including colorectal cancer, polyps, hemorrhoids, or inflammatory bowel disease.
The test involves collecting a small sample of stool, which is then analyzed in a laboratory to detect the presence of blood using chemical reagents or immunological methods. Fecal occult testing is crucial for early detection and screening of gastrointestinal disorders, aiming to facilitate prompt medical intervention and improve patient outcomes.
Analyst’s Review
Fecal occult testing presents a critical diagnostic tool for detecting gastrointestinal conditions early, notably colorectal cancer. Market growth is propelled by increasing awareness and adoption of preventive healthcare measures. Initiatives such as those promoted by the National Colorectal Cancer Roundtable and supported by recent studies are contributing to the growth of the fecal occult blood testing (FOBT).
- These efforts focus on improving colorectal cancer screening rates, particularly among the 20 million individuals receiving care at Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs).
Government support through funding, policy incentives, and educational campaigns further boosts adoption, facilitating the broader implementation of FOBT in urban community clinics, family practice networks, and healthcare systems. As healthcare systems prioritize early detection and personalized medicine, these initiatives are poised to augment sustained market expansion, thereby supporting improved patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency globally.
Fecal Occult Testing Market Growth Factors
The increasing incidence of colorectal cancer worldwide is leading to a strong demand for fecal occult testing as a pivotal screening method for early detection. As colorectal cancer ranks among the most common cancers globally, prompt identification through fecal occult tests allows for timely medical intervention, potentially improving patient outcomes and survival rates.
This non-invasive screening approach detects microscopic traces of blood in stool samples, which indicate early-stage colorectal abnormalities. With healthcare systems emphasizing preventive care and early diagnosis, fecal occult testing offers a cost-effective and accessible means to detect colorectal cancer early, thus supporting effective treatment strategies and reducing healthcare burdens associated with advanced disease stages
- According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 106,590 new cases of colon cancer in the United States are estimated to be registered in 2024 alone.
However, a significant challenge hindering the development of the fecal occult testing market is the potential for false-positive or false-negative results, which impact diagnostic accuracy and patient care. False positives may lead to unnecessary procedures and patient anxiety, while false negatives can delay necessary treatment, thereby affecting health outcomes. Key market players are addressing this challenge through technological advancements, thus enhancing test sensitivity and specificity.
They are implementing stringent quality controls, educating healthcare providers and patients on result interpretation, and integrating AI for improved analysis. Collaborations with regulatory bodies ensure adherence to standards, thereby fostering trust in test reliability. These efforts aim to mitigate testing limitations and enhance the efficacy of colorectal cancer screening programs.
Fecal Occult Testing Market Trends
Advancements in fecal occult testing technology, particularly the development of immunochemical tests (FIT), have significantly improved the accuracy and user-friendliness of screening methods. FIT tests detect human hemoglobin in stool samples with high sensitivity and specificity, distinguishing between human and non-human blood, thereby reducing false-positive results compared to traditional guaiac-based tests.
These tests are non-invasive, as they involve patients collecting a small stool sample at home, which enhances convenience and prompts higher compliance rates. Such technological advancements enhance the effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening, facilitate early detection, and are expected to drive the fecal occult testing market growth by improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs associated with advanced-stage treatments.
- For instance, the Clearview™ One Step Fecal Occult Blood Test Device (Feces) is a rapid test designed to qualitatively detect low levels of fecal occult blood (FOB). Utilizing a double antibody sandwich assay, the test selectively detects FOB at levels of 50 ng/ml or higher, or 6 µg/g of feces. Unlike guaiac assays, the accuracy of this test is not influenced by the patient's diet.
- For instance, in February 2023, Charles River Laboratories International, Inc. launched its inaugural Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Kit for detecting and quantifying residual host cell proteins (HCP) in CHO-based biotherapeutics. The HCP ELISA kit achieves industry-leading sensitivity and specificity rates, detecting levels as low as 0.1 ng/mL with 90 percent antibody coverage, due to the unique utilization of chicken immunoglobulin Y (IgY) antibodies.
Public health campaigns and favorable government initiatives advocating colorectal cancer screening have been pivotal in promoting fecal occult testing among at-risk populations. These initiatives raise awareness regarding the importance of early detection through regular screening, emphasizing the benefits of fecal occult tests in identifying colorectal abnormalities before symptoms manifest.
By targeting at-risk groups, such as individuals over 50 years old and those with a family history of colorectal cancer, these campaigns aim to reduce mortality rates by encouraging timely medical intervention. Increased adoption of fecal occult testing resulting from these efforts supports proactive healthcare practices. This empowers individuals to prioritize their colorectal health through accessible screening programs, thereby stimulating the growth of the market.
Segmentation Analysis
The global market is segmented based on test type, distribution channel, and geography.
By Test Type
Based on test type, the fecal occult testing market is categorized into guaiac fob stool test, immuno-fob agglutination test, lateral flow immuno-fob test, and immuno-fob Elisa test. The guaiac fob stool test segment garnered the highest revenue of USD 642.2 million in 2023. This diagnostic test is crucial for detecting hidden blood in stool, aiding in the early identification of colorectal cancer and other gastrointestinal disorders.
This widespread adoption is fostered by its cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and effectiveness in population screening programs. As healthcare systems prioritize preventive care and early detection, the demand for guaiac FOB stool test is expected to rise. Its proven efficacy in improving patient outcomes underscores its significant contribution to advancing diagnostic capabilities in gastrointestinal health management, thus bolstering the expansion fo the segment.
By Distribution Channel
Based on distribution channel, the market is divided into hospitals, clinical diagnostic laboratories, and others. The clinical diagnostic laboratories segment captured the largest fecal occult testing market share of 55.45% in 2023.
These laboratories provide essential services ranging from routine blood tests to advanced molecular diagnostics, catering to a wide spectrum of healthcare needs. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, aging populations, and rising demand for personalized medicine are key factors propelling segmental expansion.
Moreover, advancements in technology and automation within these laboratories enhance efficiency and accuracy, further boosting their appeal. As healthcare systems worldwide prioritize early detection and disease prevention, clinical diagnostic laboratories are poised to experience sustained growth, supported by their integral role in modern healthcare delivery.
Fecal Occult Testing Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the global market is classified into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, MEA, and Latin America.

The North America fecal occult testing market share stood around 35.67% in 2023 in the global market, with a valuation of USD 642.2 million. The region's well-established healthcare infrastructure, coupled with high healthcare expenditure per capita, contributes to the surging demand for diagnostic services. Increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disorders, along with an aging population, fuels the demand for diagnostic tests.
Technological advancements, such as next-generation sequencing and digital pathology, enhance laboratory capabilities, further supporting regional market expansion. Moreover, stringent regulatory standards ensure high-quality diagnostic services, thereby fostering trust among both healthcare providers and patients. With a growing focus on early detection and disease management, the market is expected to experience growth.
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to witness the highest growth, registering a CAGR of 6.31% over the forecast period. Rapid urbanization, increasing healthcare spending, and expanding healthcare infrastructure are major factors supporting regional market expansion. The region's large and diverse population, combined with rising incidence of infectious diseases, chronic conditions, and cancer, boosts demand for diagnostic testing services.
Moreover, technological advancements in diagnostics, such as point-of-care testing and molecular diagnostics, are aiding domestic market growth. Additionally, government initiatives aimed at improving healthcare access and quality further stimulate demand for clinical diagnostic services in the region.
Competitive Landscape
The fecal occult testing market report will provide valuable insight with an emphasis on the fragmented nature of the industry. Prominent players are focusing on several key business strategies such as partnerships, mergers and acquisitions, product innovations, and joint ventures to expand their product portfolio and increase their market shares across different regions.
Companies are implementing impactful strategic initiatives, such as expanding services, investing in research and development (R&D), establishing new service delivery centers, and optimizing their service delivery processes, which are likely to create new opportunities for market growth.
List of Key Companies in Fecal Occult Testing Market
- Abbott
- HemoCue America (Danaher company)
- QuidelOrtho Corporation
- Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc
- Biohit Oyj
- Polymedco, LLC.
- Quest Diagnostics
- Randox Laboratories Ltd
- New Day Diagnostics
Key Industry Development
- November 2022 (Product launch): Eiken Chemical Co., Ltd announced the release of the Fully Automated Faecal Immunochemical Test/Faecal Calprotectin Analyzer OC-SENSOR Ceres. This development complied with the CE Marking requirements stipulated in the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (EU) 2017/746.
The global fecal occult testing market is segmented as:
By Test Type
- Guaiac FOB Stool Test
- Immuno-FOB Agglutination Test
- Lateral Flow Immuno-FOB Test
- Immuno-FOB ELISA Test
By Distribution Channel
- Hospitals
- Clinical Diagnostic Laboratories
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- France
- U.K.
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- North Africa
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America


