Debt Financing Market Size
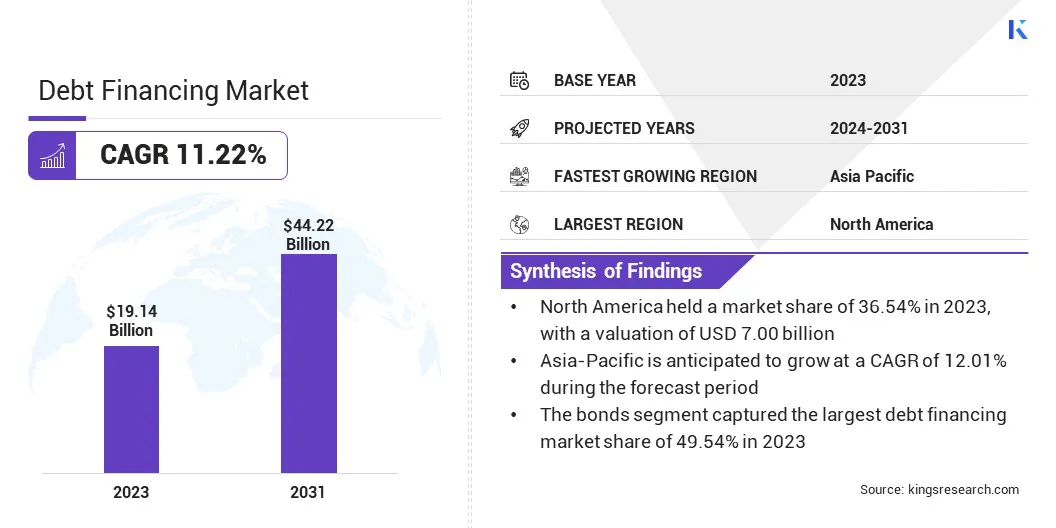
The global Debt Financing Market size was valued at USD 19.14 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 21.01 billion in 2024 to USD 44.22 billion by 2031, exhibiting a CAGR of 11.22% during the forecast period. Governments as well as private corporations using debt financing to fund large-scale infrastructure projects and the expanding private debt market are fostering market growth.
In the scope of work, the report includes services offered by companies such as Banco Santander S.A., Bank of America Corporation, Barclays, Citigroup Inc., Deutsche Bank AG, European Investment Bank, Frontier Development Capital Ltd., JPMorgan Chase & Co., Royal Bank of Canada, CREDIT SUISSE, and others.
Fintech innovations in the debt market, particularly blockchain-based bonds, are revolutionizing the debt financing market. Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and transparent nature, enhances the efficiency and security of bond transactions. These bonds are created and managed through smart contracts, which automate various processes, such as interest payments and maturity settlements, reducing the need for intermediaries and lowering transaction costs. Blockchain also allows real-time tracking and verification of bond ownership, minimizing the risk of fraud or errors.
- In September 2024, Siemens issued a new digital bond, reaffirming its leadership in FinTech and blockchain innovation within capital markets.
- In July 2024, Palau partnered with Ripple Labs to develop a US dollar-pegged stablecoin on Ripple's XRP Ledger CBDC platform, advancing a project initiated in 2021. SORAMITSU is collaborating with the Central Bank of Papua New Guinea on a CBDC proof-of-concept, aiming to establish a unified blockchain platform across the Pacific Islands.
Blockchain-based bonds offer increased transparency, speed, and accessibility for both issuers and investors. These bonds are likely to attract a broader range of participants, including smaller issuers and retail investors, who previously faced high barriers to entry in traditional bond markets. This innovation can democratize the debt financing process, opening new opportunities for capital raising and investment. Furthermore, blockchain bonds integrate with other fintech solutions, such as digital wallets and tokenized assets, broadening the scope for future growth in the debt financing landscape.
Debt financing enables an entity to raise capital by borrowing funds from external sources, typically through loans or bonds issuance. Unlike equity financing, where a company sells shares of ownership, debt financing involves a commitment to repay the borrowed amount along with interest over a predetermined period. Debt financing encompasses various types, including short-term loans, long-term loans, and bonds.
Sources of debt financing range from traditional banks, credit unions, and government-backed lenders to institutional investors and private funds. Each source has its advantages and conditions depending on the borrower's creditworthiness and needs. Short-term debt is usually intended to meet the immediate operational needs, while long-term debt, such as corporate bonds or mortgages, supports capital-intensive projects or expansion plans.
The duration and terms of debt financing agreements vary widely but are typically structured to ensure regular repayment over the life of the loan or bond. While debt financing allows companies to maintain ownership control, it also introduces financial obligations and risks if the borrower does not adhere to repayment schedules.
Analyst’s Review
The current global debt financing market shows a clear focus on innovation and strategic diversification among key players. Companies are adopting digital platforms and embracing fintech solutions to streamline debt issuance, allowing improved efficiency and lower costs. Many market leaders have also focused on expanding into sustainable finance, particularly through the issuance of green bonds, aligning their strategies with global ESG goals. The drive for sustainable investments is a notable shift, with companies positioning themselves as environmentally and socially responsible to cater to investor demand.
- In May 2024, Telephone and Data Systems closed a USD 375 million unsecured debt financing with Oaktree Capital Management. The funds are allocated for general corporate purposes, including the expansion of TDS Telecom’s fiber network, aligning with its long-term goal of reaching 1.2 million marketable fiber service units.
Additionally, expansion into emerging markets is a key growth strategy. Companies are tapping into higher-yielding debt instruments from these regions to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on the demand for infrastructure financing. However, with growing global debt levels, companies must also prioritize risk management. Adopting a cautious approach to leverage, improving credit ratings, and maintaining liquidity are crucial imperatives to ensure long-term stability. Effective risk management will be essential in navigating geopolitical and economic uncertainties that may impact the market.
Debt Financing Market Growth Factors
Governments and corporations are increasingly relying to fund large-scale infrastructure projects, which include transportation networks, energy systems, telecommunications, and public utilities to propel the debt financing market. These projects require substantial capital investment, and debt financing offers an effective means to secure the necessary funding without depleting cash reserves or increasing taxes in the case of governments.
Long-term debt instruments, such as bonds, allow entities to spread the cost of these projects over time, aligning the financial burden with the expected long-term benefits. Governments are issuing sovereign bonds, while corporations use corporate bonds or loans from institutional investors to finance these endeavors. This trend supports infrastructure development and stimulates economic growth by creating jobs, improving public services, and enhancing productivity.
Infrastructure bonds often attract institutional investors seeking stable, long-term returns, further reinforcing the capital inflow into these projects. As the demand for modern infrastructure grows, particularly in emerging markets, debt financing will continue to play a critical role in facilitating large-scale development and economic progress in the coming years.
However, geopolitical uncertainty and regulatory changes are significant challenges in the global debt financing market. Unstable political environments, shifting trade policies, and international conflicts create an atmosphere of unpredictability, affecting investor confidence and market stability. Regulatory changes, particularly in cross-border debt issuance and tax policies, introduce additional complexities that companies must navigate.
Changes in interest rates, capital controls, or restrictions on foreign investments can directly impact the cost and availability of debt financing. These factors are likely to create volatility in bond markets, particularly in emerging economies where political risk is often higher. Additionally, increasing stringency of financial regulations may limit access to capital or impose more stringent conditions on borrowing.
Companies and governments involved in debt financing must be proactive in monitoring regulatory developments and diversifying their sources of capital to mitigate these risks. To navigate this uncertainty, key players will need to implement robust risk management frameworks, engage in scenario planning, and maintain open channels of communication with regulators and policymakers to swiftly adapt to regulatory shifts.
Debt Financing Market Trends
The growing demand for green bonds as both investors and issuers prioritize environmentally sustainable projects is a pivotal trend for debt financing market. Green bonds, which are designated to fund projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and climate adaptation, are gaining significant traction in global financial markets.
Governments, corporations, and financial institutions are issuing green bonds to attract investors focused on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. This trend reflects a broader shift toward sustainable investments, as stakeholders are more conscious of the environmental and social outcomes of their financial decisions.
- As of January 2023, green bonds globally raised USD 2.5 trillion for sustainable projects, with emerging market governments contributing USD 74 billion, or 2% of the total.
Such funds are increasingly directed toward green and social initiatives, reflecting the growth of sustainable finance across markets. Increasing regulation around climate action, coupled with growing consumer awareness of corporate responsibility, is driving this demand.
Green bonds also offer issuers a way to enhance their reputation and meet corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals, while investors benefit from aligning their portfolios with sustainability initiatives. As climate change and environmental degradation remain critical global concerns, the demand for green bonds is expected to rise, providing a crucial financial mechanism for funding the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Segmentation Analysis
The global market has been segmented on the basis of type, source, duration, and geography.
By Type
Based on type, the market has been bifurcated into bank loans, bonds, and others. The bonds segment captured the largest debt financing market share of 49.54% in 2023, largely attributed to the growing reliance of both governments and corporations on bond issuances for capital raising.
Bonds, as a key debt financing tool, offer a more stable, long-term funding solution compared to short-term loans or equity financing. The market’s preference for bonds is driven by the predictable returns they offer to investors and their lower risk profile compared to equities, especially in volatile economic conditions. Governments are increasingly issuing sovereign bonds to finance large-scale public infrastructure projects and social initiatives, while corporations are leveraging corporate bonds to fund expansions, mergers, and long-term investments.
Additionally, the rise of sustainable finance, including the issuance of green bonds, has further boosted demand in the bonds segment, aligning with investor interests in environmentally and socially responsible investments. With favorable interest rates and market conditions, bonds have become the preferred choice for raising large amounts of capital, establishing their dominance in the global market.
By Source
Based on source, the market has been classified into private and public. The public segment is poised to record a staggering CAGR of 11.41% through the forecast period, reflecting the increasing need for public entities, such as governments and municipalities, to secure financing for critical infrastructure and public service projects.
Public debt financing is essential for funding projects, such as including transportation networks, healthcare systems, education, and renewable energy infrastructure, which enhance national development. The rise in public debt issuance is largely influenced by governments' focus on stimulating economic growth and addressing urgent societal needs, especially in the wake of global crises such as pandemics or climate-related challenges.
Furthermore, with historically low interest rates and increased fiscal spending policies in various regions, public debt markets are expanding rapidly. Sovereign bonds and municipal bonds are commonly utilized options, attracting both domestic and international investors seeking secure, long-term returns.
By Duration
Based on duration, the debt financing market has been divided into short-term and long-term. The long-term segment garnered the highest revenue of USD 10.85 billion in 2023, propelled by the increasing preference of corporations and governments for long-term debt instruments to finance large-scale, capital-intensive projects.
Long-term debt, typically structured over 10 years or more, is particularly attractive because it allows issuers to spread repayment obligations over an extended period, reducing short-term financial pressures. This is critical for infrastructure projects, real estate development, and major corporate investments, which require significant upfront capital but generate returns over the long term.
Investors are also drawn to long-term bonds and loans due to the steady income they provide, along with relatively lower risks associated with longer-term commitments compared to equities. The favorable interest rate environment in 2023, coupled with high demand for sustainable investments through green and climate bonds, has further accelerated the growth in this segment. This trend reflects the market’s confidence in the long-term economic outlook, as both issuers and investors seek stability and predictable returns in an uncertain global environment.
Debt Financing Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the global market has been segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, MEA, and Latin America.

North America’s debt financing market share accounted for 36.54% and was valued at USD 7.00 billion in 2023, holding a dominant position in the global market. This high share is driven by the region’s mature financial infrastructure, diverse range of debt instruments, and robust demand from both public and private sectors for capital to support infrastructure, corporate expansion, and innovation.
The U.S., in particular, plays a central role due to its deep and liquid bond markets, where both sovereign and corporate bonds are extensively issued and traded. Favorable interest rates in recent years and a strong demand for government-backed securities have further boosted debt issuance across North America.
Additionally, the region’s focus on sustainable finance, particularly through the growing issuance of green bonds, reflects the increasing integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles in investment strategies. The high creditworthiness of North American borrowers and strong investor appetite for secure, long-term returns have also helped the region maintain its position as a global hub for debt financing.
Asia-Pacific is also set to grow at a robust CAGR of 12.01% over the coming years, driven by rising infrastructure development, increasing corporate debt issuance, and improved access to global capital markets. This growth reflects the rapid economic development of major economies in the region, including China, India, and Southeast Asian nations, which are investing heavily in transportation, energy, and digital infrastructure to support long-term growth.
- For instance, in 2023, the World Bank reported that India launched its first green bond, raising USD 2 billion to fund climate change mitigation, adaptation, and conservation projects. This marks a significant step toward India's net-zero and environmental sustainability goals, supported by the World Bank’s endorsement.
The region is focusing on leveraging debt financing to meet their capital needs, as well as to fund sustainability projects, such as renewable energy and green urban development. Additionally, the region is seeing increased participation from international investors seeking higher returns in emerging markets compared to developed markets. Regulatory reforms aimed at liberalizing financial markets and improving transparency are also encouraging debt issuance in this region.
Competitive Landscape
The global debt financing market report provides valuable insights, highlighting the fragmented nature of the industry. Prominent players are focusing on several key business strategies, such as partnerships, mergers and acquisitions, product innovations, and joint ventures, to expand their product portfolio and increase their market shares across different regions.
Companies are implementing impactful strategic initiatives, such as expanding service offerings, investing in research and development (R&D), establishing new service delivery centers, and optimizing their service delivery processes, which is likely to create new opportunities for market growth. which are likely to create new opportunities for market growth.
List of Key Companies in Debt Financing Market
- Banco Santander S.A.
- Bank of America Corporation
- Barclays
- Citigroup Inc.
- Deutsche Bank AG
- European Investment Bank
- Frontier Development Capital Ltd.
- JPMorgan Chase & Co.
- Royal Bank of Canada
- CREDIT SUISSE
Key Industry Development
- October 2023 (Acquisition): Deutsche Bank AG acquired Numis Corporation Plc, creating "Deutsche Numis." This strategic move would strengthen its presence in UK investment banking and enhance itsadvisory services. The acquisition aligns with Deutsche Bank's Global Hausbank strategy, deepening its engagement with UK corporates and financial service clients.
The global debt financing market has been segmented:
By Type
By Source
By Duration
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- France
- UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- North Africa
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America

