Market Definition
A carbon credit, also referred to as a carbon offset, is a tradable certificate that represents the reduction or removal of one metric ton of carbon dioxide (CO₂) or an equivalent amount of another greenhouse gas (GHG) from the atmosphere. It is a key component of market-based mechanisms designed to incentivize emission reductions.
Organizations can purchase carbon credits to offset their own emissions, supporting projects such as reforestation, renewable energy, and carbon capture. These credits are traded in both compliance and voluntary markets, allowing businesses to meet regulatory requirements or achieve sustainability goals while supporting global climate action.
Carbon Credit Market Overview
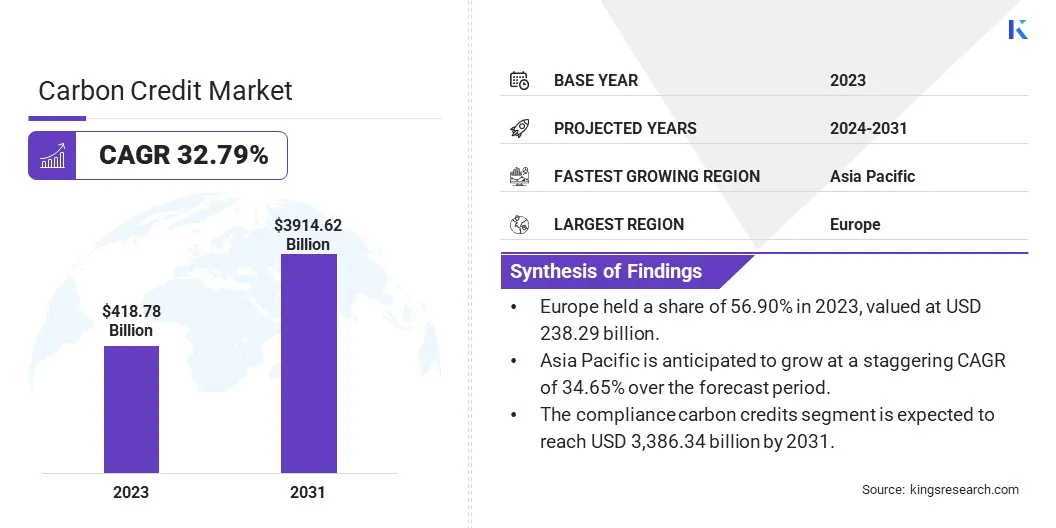
The global carbon credit market size was valued at USD 418.78 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 537.78 billion in 2024 to USD 3,914.62 billion by 2031, exhibiting a CAGR of 32.79% during the forecast period.
The growth of the market is driven by stringent government regulations and climate policies that mandate emission reductions across industries. Additionally, increasing corporate sustainability commitments are fueling demand for carbon credits as companies strive to achieve net-zero targets.
The expansion of carbon trading platforms and innovative market mechanisms is further enhancing accessibility, facilitating seamless transactions, and attracting more participants.
Major companies operating in the carbon credit industry are South Pole, 3Degrees Inc., Finite Carbon, EKI Energy Services ltd., Native, Carbon Trade Exchange (CTX), Carbon Streaming Corporation, Brookfield Renewable Partners L.P., Gold Standard, ClimateCare, Climate Partner GmbH, Climetrek, natureOffice., Tasman Environmental., ClimateTrade, and others.
Governments worldwide are enforcing stricter carbon regulations to achieve climate goals, bolstering the growth of the market. Policies such as cap-and-trade systems, carbon taxes, and mandatory emission reduction targets are compelling industries to adopt cleaner technologies and purchase carbon credits to remain compliant.
- Carbon pricing revenues hit a record USD 104 billion in 2023, as reported in the World Bank’s annual State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2024, published in May 2024.
Regulatory frameworks are continuously evolving, creating a structured environment for carbon credit trading. Countries with strong net-zero commitments are strengthening enforcement mechanisms to ensure businesses’ participation in emission reduction initiatives.
Supportive policy measures, including subsidies for carbon offset projects and cross-border trading agreements, are further boosting market expansion. While traditional sectors such as power and industry continue to dominate, carbon pricing is increasingly being considered in new sectors such as aviation, shipping, and waste.
For instance, the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, currently in a transition phase, is prompting governments to explore carbon pricing in industries such as iron and steel, aluminum, cement, fertilizers, and electricity.
 Key Highlights:
Key Highlights:
- The carbon credit industry size was recorded at USD 418.78 billion in 2023.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 32.79% from 2024 to 2031.
- Europe held a share of 56.90% in 2023, valued at USD 238.29 billion.
- The avoidance/reduction projects segment garnered USD 344.82 billion in revenue in 2023.
- The compliance carbon credits segment is expected to reach USD 3,386.34 billion by 2031.
- The power & energy segment is projected to generate a revenue of USD 1,863.14 billion by 2031.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at a staggering CAGR of 34.65% over the forecast period.
Market Driver
“Stronger Regulatory Oversight on Carbon Credit”
The introduction of standardized methodologies for carbon credit verification is supporting the growth of the carbon credit market. Regulatory frameworks such as the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS), Gold Standard, and Global Carbon Council enhance credit credibility and ensure transparency in trading activities. The establishment of robust governance models is minimizing the risks of carbon credit fraud and misrepresentation.
Governments and industry associations are working to harmonize international carbon credit policies, boosting confidence among investors and corporate participants. Stronger regulatory oversight is enhancing the legitimacy of voluntary and compliance markets, leading to increased adoption across industries.
- In February 2024, Verra advanced the development of Version 5 of the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) Program. This follows the publication of responses to feedback received during a high-level consultation on the program’s rules and requirements, conducted from February 6 to April 7, 2023. Through the VCS Program and related initiatives, Verra aims to accelerate climate action at the scale, speed, and integrity required to meet global climate objectives. Version 5 will incorporate recent updates, aligning the program with ICVCM’s Core Carbon Principles, the next phase of CORSIA, and operationalized labels for Article 6, reductions, and removals.
Market Challenge
“Lack of Standardization and Transparency”
The lack of universally accepted standards and transparency in carbon credit verification poses a significant challenge to the growth of the carbon credit market. Inconsistent methodologies for measuring, reporting, and verifying emissions reductions create credibility concerns, limiting investor confidence and corporate participation.
To address this challenge, companies are adopting blockchain technology to enhance traceability and prevent fraud in carbon credit transactions. Organizations are further aligning with globally recognized frameworks such as ICVCM’s Core Carbon Principles and Verra’s Verified Carbon Standard.
Additionally, independent third-party verification and regulatory collaboration are improving market integrity, ensuring greater accountability and trust in carbon credit trading.
Market Trend
“International Climate Agreements and Global Collaboration”
Global climate agreements are influencing the carbon credit market. Commitments under the Paris Agreement and decisions from COP summits are establishing emission reduction targets for governments and businesses.
International cooperation is facilitating the cross-border trading of carbon credits, fostering a unified approach to emissions management. Multinational corporations are aligning sustainability strategies with global climate policies, increasing participation in carbon credit programs. Carbon pricing mechanisms are gaining traction in emerging economies, expanding market reach.
- The EU-China Joint Statement on Climate Change, adopted at the 2015 EU-China summit, outlined a commitment to enhance bilateral cooperation on carbon markets. The project, initially set to conclude earlier, was extended until November 2024 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The initiative, known as the Platform for Policy Dialogue and Cooperation between the EU and China on Emissions Trading, focuses on capacity building and training to support China’s nationwide emissions trading system. On June 18, 2024, an updated MoU on Emission Trading System (ETS) cooperation was signed in Brussels by the EU Commissioner, further expanding and strengthening EU-China collaboration.
The establishment of compliance frameworks and bilateral agreements is reinforcing regulatory alignment, ensuring long-term stability in market.
Carbon Credit Market Report Snapshot
|
Segmentation
|
Details
|
|
By Project
|
Avoidance/Reduction Projects, Carbon Sequestration Projects
|
|
By Type
|
Voluntary Carbon Credits, Compliance Carbon Credits
|
|
By End User
|
Power & Energy, Industrial Manufacturing, Aviation, Agriculture, Others
|
|
By Region
|
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico
|
|
Europe: France, U.K., Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe
|
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific
|
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa
|
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America
|
Market Segmentation:
- By Project (Avoidance/Reduction Projects and Carbon Sequestration Projects): The avoidance/reduction projects segment earned USD 344.82 billion in 2023, driven by its cost-effectiveness and scalability, enabling industries to achieve significant emission reductions through initiatives such as renewable energy adoption, energy efficiency improvements, and methane capture.
- By Type (Voluntary Carbon Credits and Compliance Carbon Credits): The compliance carbon credits segment held a share of 79.55% in 2023, due to regulatory mandates and cap-and-trade programs, compelling industries to purchase credits to meet emission reduction targets and avoid penalties.
- By End User (Power & Energy, Industrial Manufacturing, Aviation, Agriculture, and Others): The power & energy segment is projected to reach USD 1,863.14 billion by 2031, mainly fueled by high emissions from fossil fuel-based power generation, which increases the demand for carbon offset initiatives and regulatory compliance to meet global decarbonization targets.
Carbon Credit Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the global market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America.
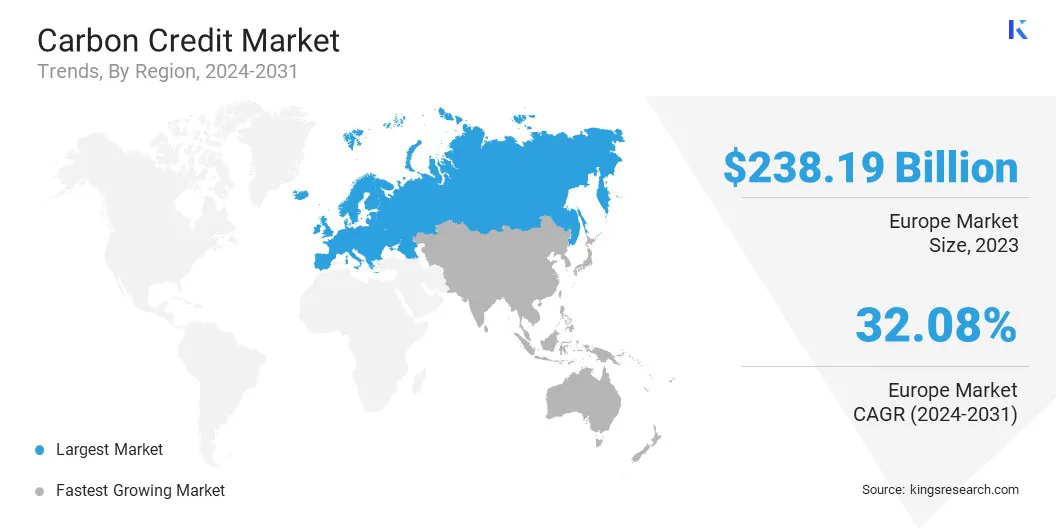 The Europe carbon credit market accounted for a notable share of around 56.90% in 2023, valued at USD 238.29 billion. The European Union's commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 is supporting this expansion.
The Europe carbon credit market accounted for a notable share of around 56.90% in 2023, valued at USD 238.29 billion. The European Union's commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 is supporting this expansion.
The EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), the largest carbon market globally, is evolving with stricter emission caps and expanded coverage, including maritime transport.
The revision of the EU ETS under the “Fit for 55” package is generating a strong demand for carbon credit as industries seek to comply with more ambitious reduction targets. Stronger regulatory enforcement and higher carbon prices are prompting businesses to invest in emissions reduction projects, influencing regional market growth.
Additionally, European governments are actively promoting carbon credit generation through investments in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies and nature-based solutions.
Funding initiatives and public-private partnerships are accelerating large-scale CCS projects, enhancing the availability of high-quality carbon credits. Additionally, reforestation and afforestation programs supported by the EU and national governments are creating verified carbon offsets.
Asia Pacific carbon credit industry is poised to grow at a robust CAGR of 34.65% over the forecast period. The inclusion of aviation and maritime emissions in carbon pricing frameworks is boosting this growth.
Airlines operating in the region are participating in the Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA), increasing demand for high-quality offsets. Shipping companies are preparing for the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) decarbonization targets by integrating carbon credits into emissions reduction strategies.
- The International Maritime Organization (IMO) and Germany's Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, and Nuclear Safety (BMU) recently signed an agreement to initiate preparatory activities for a project aimed at reducing maritime transport emissions in East and Southeast Asia. This initiative is backed by BMU’s International Climate Initiative (IKI). To advance the project, IMO will collaborate with the Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia (PEMSEA) to conduct preparatory work and develop a comprehensive project proposal.
Additionally, the establishment of carbon markets in major port cities such as Singapore is fostering a structured trading environment for maritime sector offsets, reinforcing the region’s role in global carbon credit trading.
Regulatory Frameworks:
- In Europe, the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) sets a cap on total greenhouse gas emissions from covered sectors and allows trading of emission allowances. Germany, as an EU member, participates in the EU ETS and has also implemented a national emissions trading system for sectors not covered by the EU ETS, including transportation and heating. The UK, post-Brexit, established the UK Emissions Trading Scheme (UK ETS) in 2021, similar to the EU ETS but tailored to national circumstances.
- China launched its national Emissions Trading System (ETS) in 2021, initially covering the power generation sector, making it the largest carbon market globally by volume. The system sets emission intensity benchmarks and allocates allowances based on historical emissions. Expansion to include sectors such as steel and cement is planned to support China’s carbon neutrality objectives.
- South Korea operates a national Emissions Trading Scheme (K-ETS), launched in 2015, covering key sectors such as power generation, industry, and aviation. The K-ETS sets emission caps and facilitates the trading of allowances, with mechanisms for market stabilization and incentives for early reduction efforts.
Competitive Landscape
The global carbon credit market is characterized by a large number of participants, including both established corporations and emerging players. Leading companies in the market are actively forming strategic partnerships to enhance their sales channels and expand their distribution networks across multiple regions.
These collaborations enable companies to strengthen their market presence, improve accessibility to carbon credit solutions, and tap into new customer bases. By leveraging the expertise and networks of regional partners, businesses can navigate regulatory frameworks more effectively and streamline the trading of carbon credits.
Additionally, these alliances facilitate the development of innovative carbon offset projects, ensuring a steady supply of high-quality credits to meet the rising demand. Such initiatives are significantly contributing to the overall growth of the market.
- In November 2023, Green Carbon entered into a distributor and sales partner agreement in Japan with India-based EKI Energy Services Ltd. EKI is the first Indian company accredited with Verra credits and has offset over 200 million tons of carbon dioxide. The company provides sustainable solutions for climate change and carbon offsets, adhering to global standards such as CDM, VCS, Gold Standard, GCC, IREC, and TIGR.
List of Key Companies in Carbon Credit Market:
- South Pole
- 3Degrees Inc.
- Finite Carbon
- EKI Energy Services ltd.
- Native
- Carbon Trade Exchange (CTX)
- Carbon Streaming Corporation
- Brookfield Renewable Partners L.P.
- Gold Standard
- ClimateCare
- Climate Partner GmbH
- Climetrek
- natureOffice.
- Tasman Environmental.
- ClimateTrade
Recent Developments (Partnerships/Agreements/New Product Launch)
- In February 2024, Finite Carbon introduced its digital platform, the Finite Carbon Marketplace. This marketplace was created to establish a direct, transparent, and efficient link between carbon offset buyers and premium forest carbon projects exclusively developed by Finite Carbon.
- In November 2024, EKI Energy entered into a strategic representative agreement with U.S.-based FBO Resource Group, Inc., operating as Aviation Resource Group International (ARGI). This partnership aims to expand EKI’s carbon credit trading and sustainability services across North America, with a strong emphasis on the aviation sector.
- In September 2024, Sustainiam partnered with Brookfield Asset Management to integrate a 400 MW portfolio of renewable energy assets for carbon credit generation. This portfolio consists of 50 projects, primarily wind energy facilities, situated in states including Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Rajasthan. The agreement is set to last for five years.
- In June 2023, Tasman Environmental Markets secured a groundbreaking collateralized trading facility for carbon credits for refinancing. As part of an agreement with Catalytic Impact Capital, TEM successfully refinanced its trading facility with a two-year, USD 10 million arrangement. The agreement also includes an additional USD 2.5 million in funding for TEM.

 Key Highlights:
Key Highlights: The Europe carbon credit market accounted for a notable share of around 56.90% in 2023, valued at USD 238.29 billion. The European Union's commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 is supporting this expansion.
The Europe carbon credit market accounted for a notable share of around 56.90% in 2023, valued at USD 238.29 billion. The European Union's commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 is supporting this expansion.