enquireNow
Hydrogen Rocket Engine Market
Hydrogen Rocket Engine Market Size, Share, Growth & Industry Analysis, By Engine (Expander-cycle, Gas-generator, Staged Combustion, Others), By Stage (First Stage, Upper Stage, Multi-purpose), By Application (Space Launch, Military & Defense), By End User, and Regional Analysis, 2025-2032
pages: 180 | baseYear: 2024 | release: August 2025 | author: Sunanda G.
Market Definition
A hydrogen rocket engine uses liquid hydrogen as fuel and liquid oxygen as an oxidizer, generating thrust through high-velocity exhaust from combustion. It delivers high specific impulse, clean emissions with only water vapor as a by-product, and strong performance in both space and atmospheric conditions.
The market covers applications in orbital launch vehicles, deep space exploration, and reusable rocket programs by government and commercial operators. Manufacturers design these engines for heavy-lift launches, satellite deployment, crewed missions, and advanced multi-stage propulsion systems to meet growing demand for efficient and sustainable space transportation.
Hydrogen Rocket Engine Market Overview
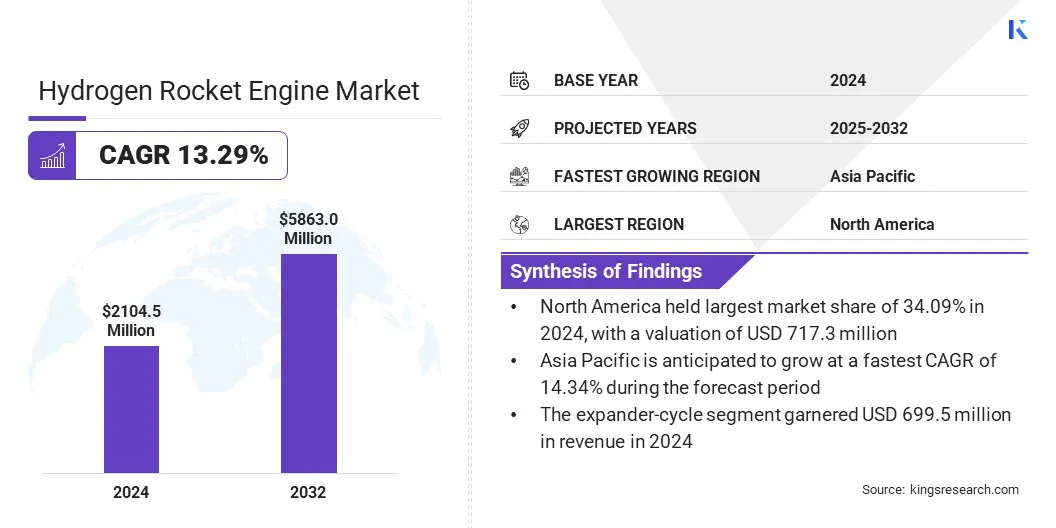
The global hydrogen rocket engine market size was valued at USD 2,104.5 million in 2024 and is projected to grow from USD 2,344.4 million in 2025 to USD 5,863.0 million by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 13.29% during the forecast period.
This growth is driven by the strategic investments in next-generation launch systems by government and private entities. Additionally, advancements in cryogenic engines featuring advanced cycles are enhancing engine efficiency and performance.
Key Highlights
- The hydrogen rocket engine industry size was USD 2,104.5 million in 2024.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.29% from 2025 to 2032.
- North America held a share of 34.09% in 2024, valued at USD 717.3 million.
- The expander-cycle segment garnered USD 699.5 million in revenue in 2024.
- The first stage segment is expected to reach USD 2,446.3 million by 2032.
- The space launch segment secured the largest revenue share of 54.02% in 2024.
- The commercial space operators segment is estimated to grow at a robust CAGR of 13.51% through the forecast period.
- Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 14.34% over the forecast period.
Major companies operating in the hydrogen rocket engine market are Blue Origin, MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD., and Arianegroup.
The increasing implementation of commercial and governmental space programs is boosting the adoption of hydrogen-fueled rocket engines.
- According to the Space Foundation report, 2024 recorded 259 launches, averaging one every 34 hours, five hours faster than in 2023. This growth is expected to fuel in 2025, supported by site upgrades, higher launch frequencies, and the debut of 24 launch vehicles. Military spacecraft deployments rose by 86% in 2024, with SpaceX launching over 100 satellites for the NRO’s Starshield constellation.
Hydrogen engines are favored for their exceptionally high specific impulse, enabling efficient long-distance missions, and their clean combustion, which produces only water vapor as exhaust.
As agencies and private space companies prioritize sustainable propulsion technologies, hydrogen engines are emerging as a preferred choice for reducing the environmental footprint of launches. Their applicability in deep-space exploration, satellite deployment, and reusable launch systems positions them as a critical component of the evolving space economy.
Market Driver
Substantial Investments From Public Space Agencies
Significant funding from public space agencies, including the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the European Space Agency (ESA), and private aerospace companies such as Blue Origin, ArianeGroup, and the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT), is accelerating the advancement of hydrogen-fueled rocket engines.
These investments are fostering advancements in engine efficiency, reusability, and manufacturing capabilities, enabling their integration into next-generation launch vehicles. The fundings reflect a major focus on enhancing higher payload capacities, reducing launch costs, and achieving sustainability through clean-burning propulsion technologies.
- In January 2025, Blue Origin conducted the maiden launch of its New Glenn rocket for the first time, featuring the BE-3U hydrogen-fueled upper stage engine. This vacuum-optimized version of Blue Origin’s BE-3 delivers high specific impulse for orbital missions, powering the rocket's second stage for applications such as satellite deployment and deep-space transportation.
Market Challenge
Cryogenic Fuel Handling and Storage Complexity
A key challenge hindering the progress of the hydrogen rocket engine market is the handling and storage of liquid hydrogen. Maintaining hydrogen at extremely low temperatures demands specialized cryogenic insulation and containment systems, which significantly increase infrastructure costs. The low energy density of hydrogen further complicates storage design, and its interaction with certain materials can lead to brittleness, posing operational risks.
To address this challenge, market players are investing in advanced cryogenic tank designs, improved insulation materials, and robust operational protocols to ensure safe and efficient fuel management. These measures are enabling gradual improvements in system reliability and reducing long-term operational inefficiencies in hydrogen-based propulsion projects.
Market Trend
Advancement of Next-Generation Cryogenic Engines with Advanced Cycles
The hydrogen rocket engine market is witnessing a notable trend toward improved cryogenic engine designs utilizing advanced thermodynamic cycles to improve thrust, thermal efficiency, and safety through optimized fuel-oxidizer mixing and heat utilization. These innovations meet the growing demand for reliable, high-performance propulsion in heavy-lift and reusable launch vehicles, aiding market expansion.
- In December 2024, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation successfully conducted the first full-system test of the YF-90 liquid hydrogen–oxygen engine in Xi’an. Designed for the second stage of the Long March 9 heavy-lift launch-vehicle, the YF-90 employs a staged combustion cycle.
Hydrogen Rocket Engine Market Report Snapshot
|
Segmentation |
Details |
|
By Engine |
Expander-cycle, Gas-generator, Staged Combustion, Others |
|
By Stage |
First stage, Upper stage, Multi-purpose |
|
By Application |
Space Launch, Military & Defense |
|
By End User |
Government Agencies, Commercial Space Operators |
|
By Region |
North America: U.S., Canada, Mexico |
|
Europe: France, UK, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe | |
|
Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, India, Australia, ASEAN, South Korea, Rest of Asia-Pacific | |
|
Middle East & Africa: Turkey, U.A.E., Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Rest of Middle East & Africa | |
|
South America: Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America |
Market Segmentation
- By Engine (Expander-cycle, Gas-generator, Staged Combustion, and Others): The expander-cycle segment earned USD 699.5 million in 2024, mainly due to its high efficiency, reliable cooling method, and suitability for upper-stage applications requiring precise thrust control and extended burn times.
- By Stage (First stage, Upper stage, and Multi-purpose): The first stage segment held a share of 42.17% in 2024, fueled by its critical role in providing the high thrust needed for liftoff, creating strong demand for powerful and reliable hydrogen-fueled engines in initial launch phases.
- By Application (Space Launch and Military & Defense): The space launch segment is projected to reach USD 3,132.0 million by 2032, fueled by surging demand for efficient, high-performance propulsion systems essential for payload deployment and expanding commercial and government space missions.
- By End User (Government Agencies and Commercial Space Operators): The commercial space operators segment is set to grow at a CAGR of 13.51% through the forecast period, largely attributed to increasing adoption of efficient, reusable propulsion technologies that support frequent launches and reduce operational costs in the expanding private space industry.
Hydrogen Rocket Engine Market Regional Analysis
Based on region, the market has been classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America.
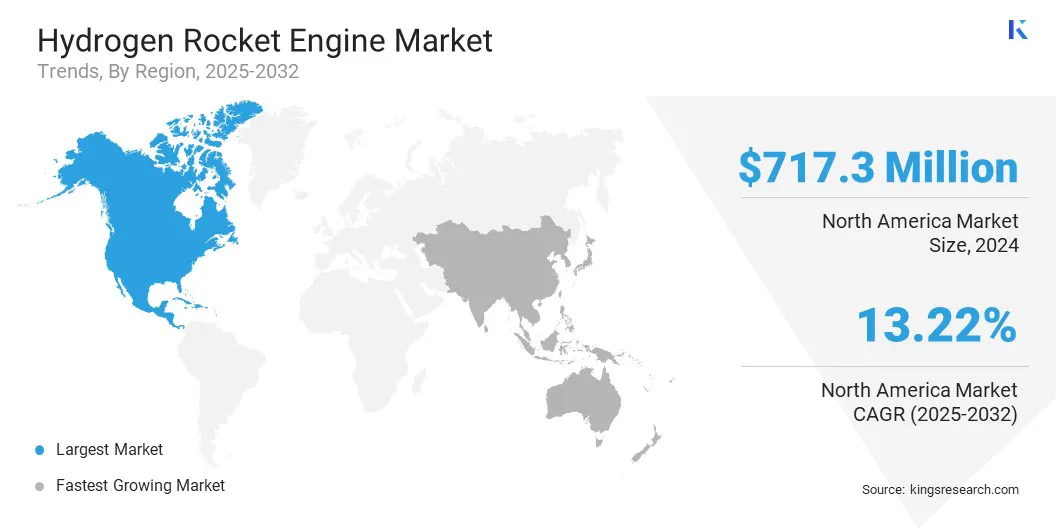
North America hydrogen rocket engine market share stood at 34.09% in 2024, with a valuation of USD 717.3 million. This dominance is reinforced by steady investments in government-led space missions. Agencies such as NASA are continuing to fund programs that rely on high-performance cryogenic propulsion, including the Space Launch System (SLS) and Artemis missions.
Moreover, major launch facilities such as Kennedy Space Center and Vandenberg Space Force Base are undergoing upgrades to handle more frequent hydrogen-fueled launches. This includes expanded cryogenic storage capacity, enhanced fueling systems, and safety improvements for handling large volumes of liquid hydrogen. These infrastructure developments reduce turnaround times between launches, supporting regional market growth.
- In July 2024, NASA moved the Space Launch System core stage to the Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The stage, housing liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen propellant tanks for the Artemis program, was transferred as part of launch preparations and infrastructure upgrades to handle large volumes of cryogenic propellants.
The Asia-Pacific hydrogen rocket engine industry is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 14.34% over the forecast period. This growth is due to the countries in Asia Pacific countries expanding their own space capabilities, with regional agencies and companies developing hydrogen-powered upper-stage engines for heavier payloads and longer missions.
- In July 2025, Hyderabad-based spacetech startup Stardour successfully test-fired India’s first indigenously developed hydrogen-oxygen (LOX–LH₂) propulsion engine. The 1 kN-class cryogenic thruster achieved over 95% combustion efficiency and is capable of multiple restarts.
Indigenous hydrogen propulsion programs aim to reduce reliance on foreign technology, which accelerates domestic R&D and supports frequent launch schedules. This shift toward self-reliance is boosting hydrogen engine demand. Additionally, several new spaceports and launch facilities across Asia Pacific are incorporating cryogenic fueling infrastructure, including liquid hydrogen storage and transfer systems.
Regulatory Frameworks
- In the U.S., the Department of Energy’s Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies Office governs hydrogen fuel regulations, emphasizing safety, environmental standards, and technological development for aerospace applications. NASA enforces strict safety protocols for handling cryogenic fuels such as liquid hydrogen during rocket engine testing and launches.
- The Civil Aviation Authority regulates airspace and launch safety, overseeing rocket launches involving hydrogen propulsion. The Health and Safety Executive governs workplace safety, including the handling and storage of cryogenic fuels in engine manufacturing and testing facilities, ensuring compliance with national health and environmental standards.
- China’s National Space Administration and China Aerospace Corporation regulate hydrogen rocket engine development, focusing on safety, reliability, and cryogenic fuel handling. The Export Control Law restricts the export of aerospace components related to hydrogen propulsion, reflecting national security and technology protection priorities.
- India’s Department of Space mandates strict safety and environmental regulations for hydrogen rocket engine development and testing. These regulations ensure safe handling of cryogenic fuels, minimize environmental impact, and promote indigenous propulsion technology aligned with national space goals.
Competitive Landscape
Major players in the hydrogen rocket engine industry are focusing on research and development, forming strategic partnerships, and technological advancements to maintain competitiveness. Investments are directed toward improving hydrogen combustion technology and optimizing engine designs to meet evolving performance and environmental standards.
Collaborations with technology firms and aerospace agencies are accelerating innovation, reducing time to market, strengthening leadership in the growing hydrogen propulsion sector.
- In October 2024, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. successfully tested a small aircraft engine powered entirely by hydrogen. This test, aimed at advancing hydrogen technologies for next-generation aircraft, involved modifying a standard jet fuel engine with a newly developed hydrogen combustor and associated components.
Key Companies in Hydrogen Rocket Engine Market:
- Blue Origin
- MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD.
- Arianegroup
Recent Developments (Testing)
- In September 2023, Stoke Space completed a developmental test flight of its reusable second-stage rocket, demonstrating vertical takeoff and landing. The test validated the company’s hydrogen/oxygen engine, regeneratively cooled heat shield, and differential throttle thrust vector control system. This design aims to enable a fully reusable rocket with a 24-hour turnaround time.
freqAskQues
